Figure 5.
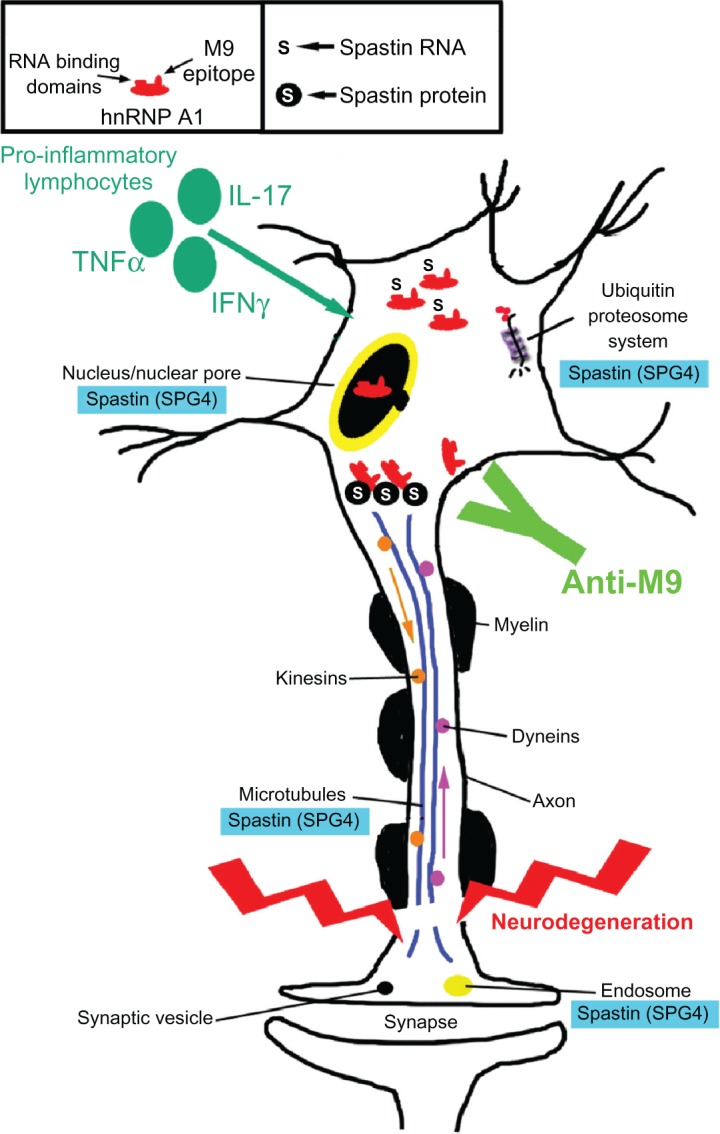
Potential contribution of the anti-heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A1 M9 immune response to neurodegeneration in immune-mediated neurological disease. Multiple sclerosis and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis patients develop antibodies to an epitope contained within the M9 region of hnRNP A1 (box). hnRNP A1 has been shown to interact molecularly with spastin RNA and protein (box and figure). The anti-M9 immune response altered spastin RNA levels, which may alter spastin function at multiple sites within neurons (blue boxes). The combination of proinflammatory cytokines and the anti-M9 immune response might contribute to neurodegeneration in immune-mediated neurological disease.
Abbreviations: TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; SPG, spinal paraplegia gene.
