Table 1.
Postural adjustments for regulating the direction and flow of ingested materials to make pills easier to swallow wholea
| Posture | Description | Comments | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
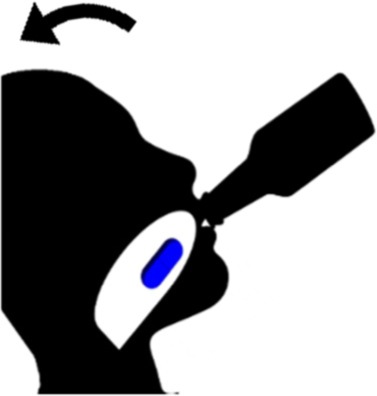
| Pop-bottle | • Place a tablet on the tongue, and swallow it with water from a flexible container through a suction motion while tilting the head back • Helps movement of the bolus from the front of the mouth to the back |
• Nearly 60% of healthy participants, with 55% of them self-reporting difficulty swallowing pills, reported improved medication swallowing ability17 • Not considered safe in patients with dysphagia due to risk of aspiration as it encourages head back posture that opens the entrance to the airways • The most preferred position by children (36%) with pill-swallowing difficulties18 |
|
| Lean-forward (chin down or chin tuck) | • Place a capsule on the tongue and take a sip of water, bend the head forward and tuck the chin toward the chest, and then swallow the capsule with the water • Enhances the protective function of epiglottis. Widens the valleculae, narrows the airway, and allows the epiglottis to be further pushed toward the back of the throat |
• Improved swallowing ability in 90% of participants in a mixed sample of people with and without pill- swallowing difficulties in one study17 • In another study, 33% of the participants with pill- swallowing difficulties endorsed this position18 • Although it has shown to prevent aspiration in 32%–55% of patients with dysphagia, the risk still exists when this technique is used in these patients16,19,20 • No evidence available around the effectiveness of this technique in pill-swallowing in patients with dysphagia |

|
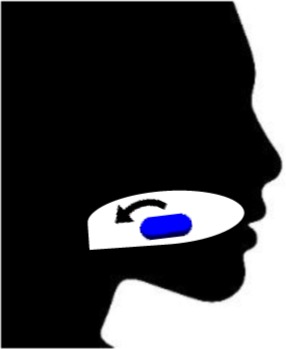
| Central head posture | • Keep the head straight with no rotation or bending | • Improved swallowing ability in 33% of otherwise healthy people with pill-swallowing difficulties only18 • No evidence available about the safety and efficacy in medication swallowing difficulty due to dysphagia |
|
Note:
Not recommendable for patients with dysphagia without thorough clinical evaluation.
