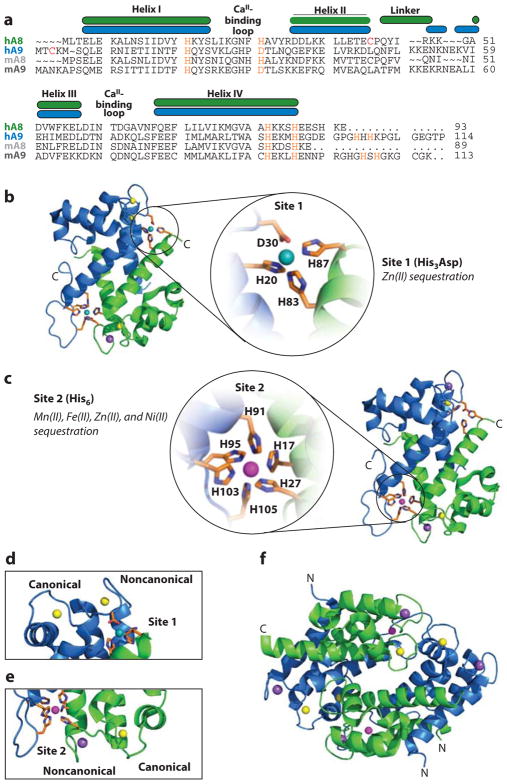
Figure 2.
Structure of human calprotectin (CP). S100A8 subunits are green, and S100A9 subunits are blue. (a) Amino acid sequence alignment of human (h) and murine (m) CP. The secondary structural elements are presented above the alignment for the human form. The transition metal–binding residues are presented in orange. For the murine S100A9 subunit, His105 and His107 are predicted to contribute to the His6 site. (b) The heterodimer bound to Ni(II) (teal ), Ca(II) ( yellow), and Na(I) ( purple) [Protein Data Bank (PDB) 5W1F]. Site 1 is expanded to show the Ni(II)-bound His3Asp motif. (c) The dimer bound to Mn(II) (magenta), Ca(II) ( yellow), and Na(I) ( purple) (PDB 4XJK). Site 2 is expanded to show the Mn(II)-bound His6 motif. (d ) S100A9 canonical and noncanonical EF-hands and proximity to the Ni(II)-bound His3Asp site (site 1) (PDB 5W1F). Both EF-hands are Ca(II) bound. (e) S100A8 canonical and noncanonical EF-hands and proximity to the Mn(II)-bound His6 site (site 2) (PDB 4XJK). The canonical EF-hand is Ca(II) bound, and the noncanonical EF-hand is Na(I) bound. ( f ) The Ca(II)-, Na(I)-, and Mn(II)-bound (S100A8/S100A9)2 tetramer (PDB 4XJK). Panel a modified from Reference 50.