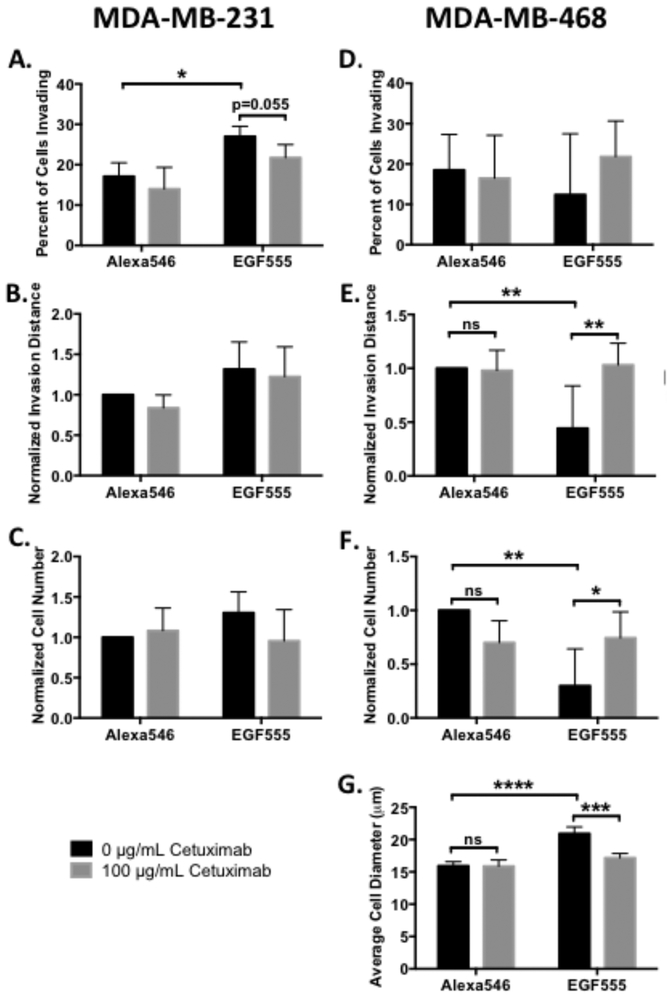
Figure 8.
Cetuximab differentially affects MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cell invasion and cell number. Post hoc comparisons are depicted graphically. A) Percent of invading MDA-MB-231 cells in low concentration gradient HANBDF/MMPx hydrogels of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg mL−1 of cetuximab (day 3, n=4, mean + standard deviation). EGF555 significantly increased the percent of MDA-MB-231 cells invading into the gradients relative to Alexa546 gradients (***p<0.001, two-way ANOVA), while cetuximab significantly decreased the percent of invading MDA-MB-231 cells relative to no treatment (*p<0.05, two-way ANOVA). B) Normalized invasion distance of MDA-MB-231 cells on low gradients of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg mL−1 of cetuximab (day 3, n=4, mean + standard deviation). C) Normalized cell number of MDA-MB-231 cells were similar on low gradients of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg mL−1 of cetuximab (day 3, n=4, mean + standard deviation). D) Percent of invading MDA-MB-468 cells in low concentration gradient HANBDF/MMPx hydrogels of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg mL−1 of cetuximab (day 6, n=5, mean + standard deviation). E) Normalized invasion distance of MDA-MB-468 cells on low gradients of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg/mL of cetuximab (day 6, n=5, mean + standard deviation). Cetuximab treatment increased MDA-MB-468 cell invasion relative to no treatment (*p<0.05, two-way ANOVA). F) Normalized cell number of MDA-MB-468 cells on low gradients of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg/mL of cetuximab (day 6, n=5, mean + standard deviation). Cetuximab treatment increased MDA-MB-468 cell number relative to no treatment (**p<0.01, two-way ANOVA). G) Average MDA-MB-468 cell diameter on low gradients of Alexa546 or EGF555 treated with either 0 or 100 μg/mL of cetuximab (day 6, n=4, mean + standard deviation). Cetuximab treatment decreased MDA-MB-468 cell diameter relative to no treatment (***p<0.001, two-way ANOVA).