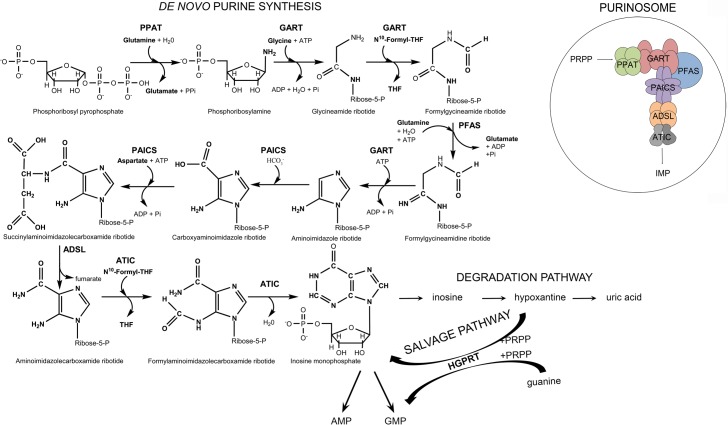
Fig 1. Scheme of de novo purine synthesis (DNPS), the salvage pathway, the degradation pathway and the purinosome.
The initial substrate in DNPS is phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). Six enzymes are involved in DNPS and the purinosome multienzyme complex: phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amidotransferase (PPAT), the trifunctional enzyme GART (glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase/glycinamide ribonucleotide transformylase/aminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase), phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthetase (PFAS), the bifunctional enzyme PAICS (phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase/phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthetase), adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), and the bifunctional enzyme ATIC (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide transformylase/inosine monophosphate cyclohydrolase). The final product is inosine monophosphate (IMP). IMP is converted into adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP) and is also degraded to uric acid via the degradation pathway. The hypoxanthine intermediate can be recycled by the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) into IMP or GMP.