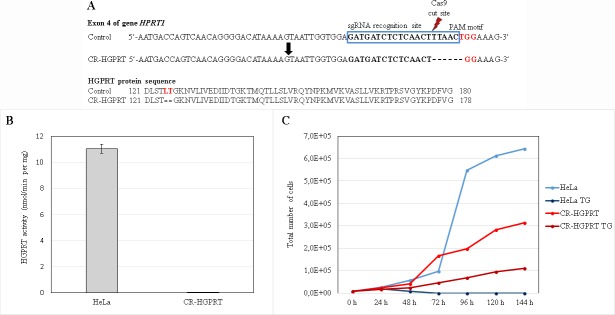
Fig 2. Characterization of the HGPRT knockout cells.
(A): Illustration of the sgRNA targeting sequence in exon 4 of the HPRT1 gene in control and CR-HGPRT cells and the protein sequences of wild-type and mutated HGPRT. The 20-bp target sgRNA sequence is indicated in the blue box, adjacent to the NGG (TGG) PAM motif sequence (red coloured). The probable Cas9 cut site is indicated by the red flash-shaped object. CR-HGPRT is shown with the appropriate c.373-378delTTAACT mutation. In the HGPRT protein sequence, the affected amino acids are coloured red; the CR-HGPRT protein shows a p. 125-126del deletion. (B): The activity of the HGPRT enzyme was determined in the control and CR-HGPRT cells. The activity of the enzyme in the CR-HGPRT cells was 0% of the activity in the control cells (n = 3). (C): Growth curves of CR-HGPRT cells and control HeLa cells. The cells were grown in normal growth medium and in growth medium containing 0.03 mM thioguanine (TG). The CR-HGPRT cells grew in the normal growth medium (light red line) and more slowly in the growth medium containing TG (dark red line). All the control cells in the medium containing TG died within 72 h (dark blue line), while the control cells in the normal medium showed ten times more growth at the same time point (light blue line).