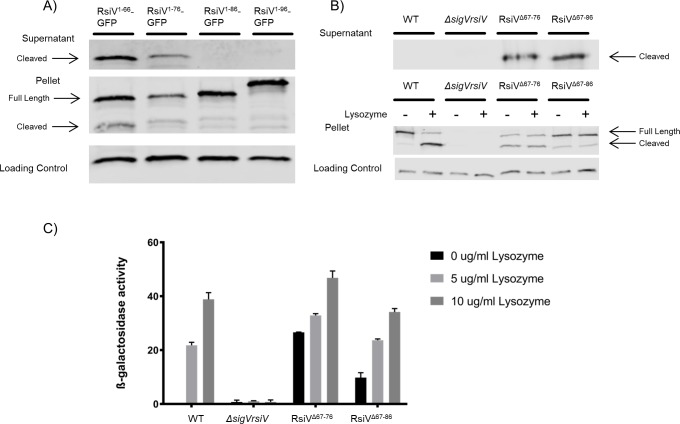
Fig 2. Amino acids after the cleavage site are involved in the protection of RsiV from signal peptidase cleavage.
A. Cells producing various lengths of N-terminal RsiV (1–66, 1–76, 1–86 and 1–96) fused to GFP were grown to mid log. Cell pellets and the supernatants were collected and analyzed by western blot with α-RsiV59-258 antibodies. Streptavidin IR680LT was used detect PycA which served as a loading control [67]. The color blot showing both pellet and loading control on a single gel is S2 Fig. B. Deletions in RsiV after the cleavage site were created (RsiVΔ67–76, RsiVΔ67–86) and expressed under an IPTG inducible promoter. The supernatants were collected. The cells were then exposed to -/+ lysozyme (10μg/mL). Samples were analyzed by western blot with α-RsiV59-258 antibodies and streptavidin IR680LT was used to detect PycA as a loading control [67]. The color blot showing both pellet and loading control on a single gel is S3 Fig. C. The deletion constructs (RsiVΔ67–76, RsiVΔ67–86) were created in a strain that carries a PsigV-lacZ reporter. σV activity was determined by measuring β-galactosidase activity. This experiment was done in triplicate and standard deviation is represented by error bars.