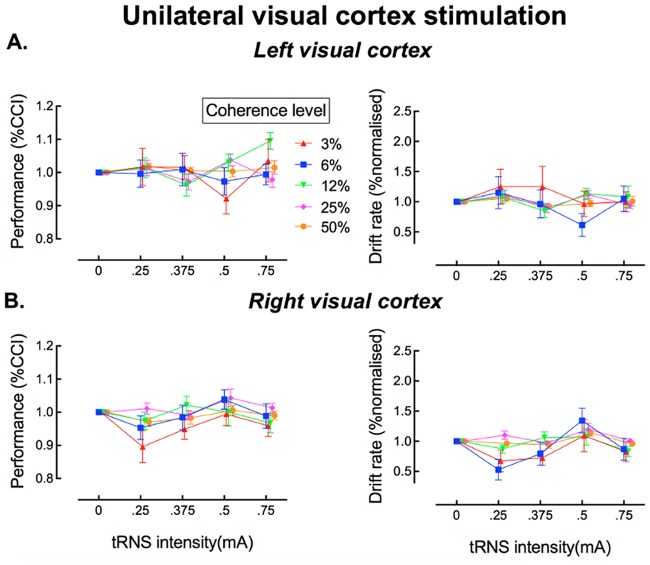
Fig 5. Effects of transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) on perceptual decision-making in the dot-motion discrimination task for unilateral stimulation of the left visual cortex (A) and right visual cortex (B).
The left panels show performance for each motion coherence level as a function of tRNS intensity. The right panels show the drift rate derived from modelling of the data shown in the corresponding plots to the left.