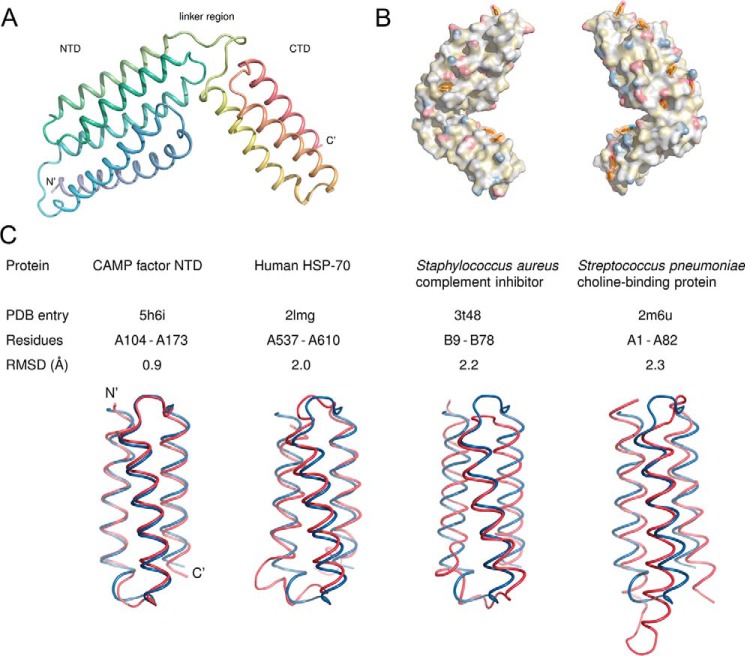
Figure 1.
Structure of GBS CAMP factor. A, overall structure. The protein consists of two helical domains connected by a linker. The N terminus in the structure is formed by residue Val41; the preceding residues were not resolved. B, aromatic residues and polar moieties on the surface of the CAMP factor molecule. Aromatic residues are shown in a stick representation and with semitransparent surfaces; the remainder of the molecule is shown as an opaque surface. Polarity is highlighted using the YRB scheme (56), which shows the side-chain nitrogens of lysine and arginine in blue, the side-chain oxygens of aspartate and glutamate in red, carbons not linked to oxygen or nitrogen atoms in yellow, and everything else without color. C, structural alignment of the CAMP factor CTD (blue) with helices 3–5 of the NTD (red) and with domains of three other proteins that belong to group 46996 of the SCOP database (24). The alignments were carried out with PyMOL.