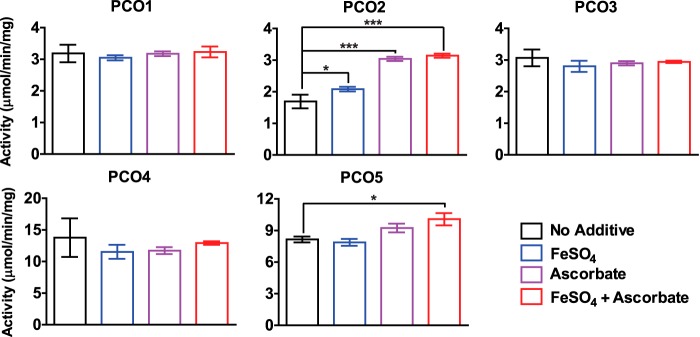
Figure 2.
Analyzing the influence of exogenous iron and ascorbate on AtPCO activity. The specific activities of AtPCOs 1–5 were determined with and without FeSO4 (100-fold in excess of enzyme concentration) and sodium ascorbate (1 mm) by measuring the rate of AtRAP2(2–15) cysteine oxidation at regular time intervals (0, 30, 60, and 90 s) by LC-MS. The addition of exogenous additives, particularly ascorbate, significantly increased the specific activities of AtPCO2 and, to a lesser extent, AtPCO5 but had little effect on the other isoforms. AtPCOs 4 and 5 had the greatest specific activity. Reactions were conducted in 50 mm HEPES, 50 mm NaCl, and 1 mm TCEP, pH 7.5, at 25 °C. Statistical analysis was completed using a one-way analysis of variance, post hoc Dunnett test using the “no additive” sample as the control reference with * and *** denoting p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.001, respectively. Error bars display S.D. (n = 3).