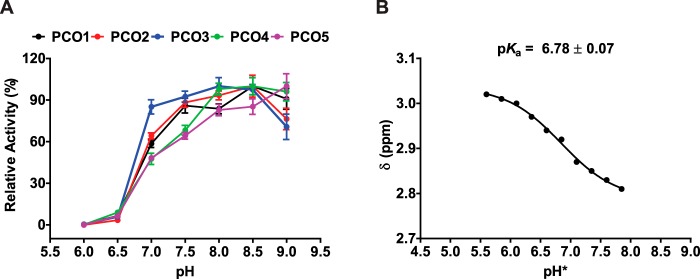
Figure 3.
The activity of AtPCOs 1–5 depends on pH. A, pH profile showing the relative activities of AtPCOs 1–5 with 200 μm RAP2(2–15) at 25 °C and different pH values using 50 mm Bis tris propane, 50 mm NaCl, and 5 mm TCEP as buffer. A significant reduction in AtPCO activity is observed below pH 7.0 for all isoforms. This correlates with the side-group pKa for the N-terminal cysteine of RAP2(2–15) (B), which was determined by monitoring the chemical shift of cysteine β-protons in D2O (>95%) using 1H NMR. This suggests that the thiol needs to be deprotonated for binding and/or turnover. pH* denotes the pH reading given by a pH meter calibrated for solutions in H2O for D2O samples. pKa was corrected to H2O using the formula pKH = 0.929pKH* + 0.42 derived in Ref. 41. Error bars display S.E. (n = 3).