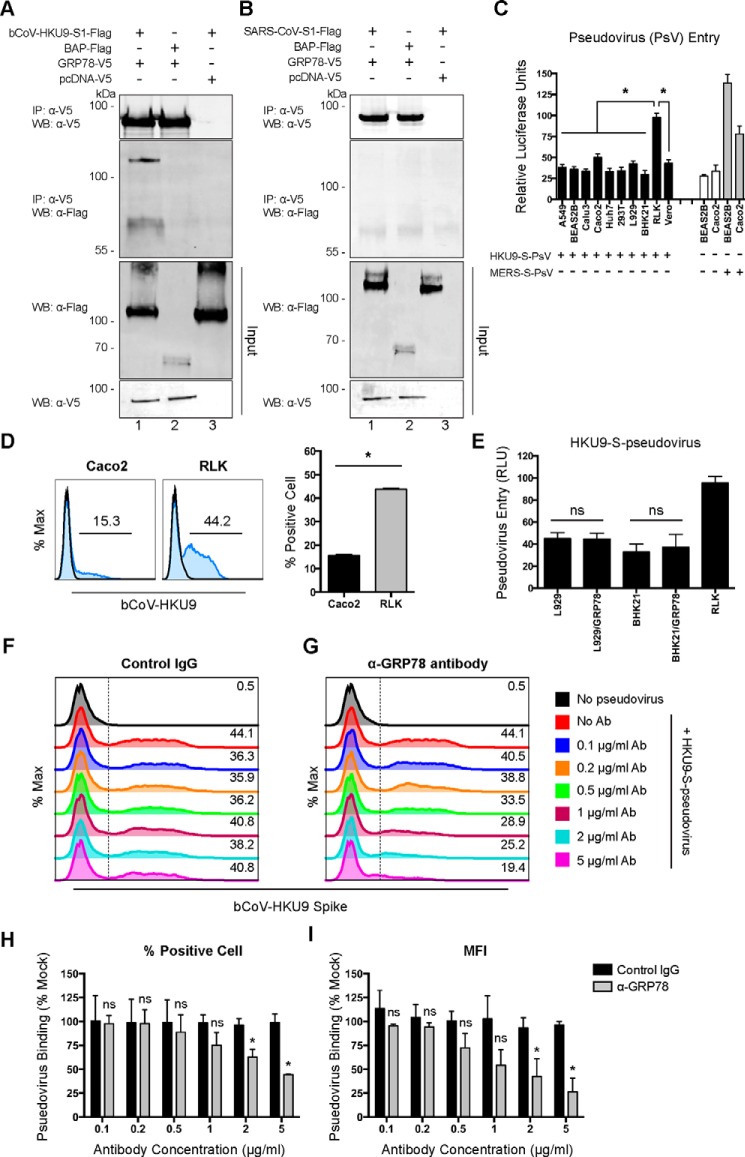
Figure 8.
GRP78 interacts with the bCoV-HKU9 spike and serves as an attachment factor for bCoV-HKU9. A, BHK21 cells were transfected with pcDNA–GRP78–V5 (lanes 1 and 2) or empty vector (lane 3). Co-IP between GRP78 and bCoV-HKU9 spike was performed using GRP78 as the bait protein. Purified bCoV–HKU9–S1–FLAG (lanes 1 and 3) or BAP–FLAG proteins (lane 2) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with overexpressed GRP78–V5 or pcDNA–V5 proteins pre-adsorbed on anti-V5–Sepharose beads. The precipitated protein complex was detected using the anti-V5 antibody or the anti-FLAG antibody. B, co-IP between GRP78 and SARS-CoV spike was performed using GRP78 as the bait protein. Purified SARS-CoV–S1–FLAG (lanes 1 and 3) or BAP–FLAG proteins (lane 2) were immunoprecipitated with overexpressed GRP78–V5 or pcDNA–V5 proteins pre-adsorbed on anti-V5–Sepharose beads. The precipitated protein complex was detected using the anti-V5 antibody or the anti-FLAG antibody. C, HKU9–S-pseudovirus entry assays were performed in a number of mammalian cell lines. Mock-inoculated and MERS–S-pseudovirus–inoculated cells were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. HKU9–S-pseudovirus and MERS–S-pseudovirus were added at a ratio of 100 LP per cell for 1 h. Luciferase activity was determined at 72 h post-inoculation. D, HKU9–S-pseudovirus attachment efficiency was evaluated in Caco2 and RLK cells. HKU9–S-pseudovirus was inoculated on Caco2 and RLK cells at 100 LP per cell for 2 h at 4 °C. After 2 h, the cells were washed, fixed, and immunolabeled for flow cytometry. HKU9–S-pseudovirus binding was identified with an in-house mouse bCoV-HKU9 spike immune serum. E, HKU9–S-pseudovirus entry in L929 and BHK21 cells was assessed with or without GRP78 overexpression. HKU9–S-pseudovirus was inoculated at 100 LP per cell for 1 h at 37 °C. Luciferase activity was determined at 72 h post-inoculation. F and G, antibody-blocking assay for HKU9–S-pseudovirus binding was performed in RLK cells. RLK cells were pre-incubated with the rabbit anti-GRP78 antibody and the rabbit control IgG from 0 to 5 μg/ml. After the pre-incubation, HKU9–S-pseudovirus was inoculated to the cells at 100 LP per cell for 2 h at 4 °C. The cells were then washed, fixed, and immunolabeled for flow cytometry. HKU9–S-pseudovirus binding was identified with an in-house mouse bCoV-HKU9 spike immune serum. The percentage of bCoV-HKU9 spike-positive cells was quantified in H, and the MFI of the bCoV-HKU9 spike on the cell surface was quantified in I. Gates in D, F, and G represented the percentage of HKU9 spike-positive cells. Data represented mean and S.D. derived from three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were carried out using Student's t test. Statistical significance was indicated by asterisks when p < 0.05. WB, Western blot. ns means not significant.