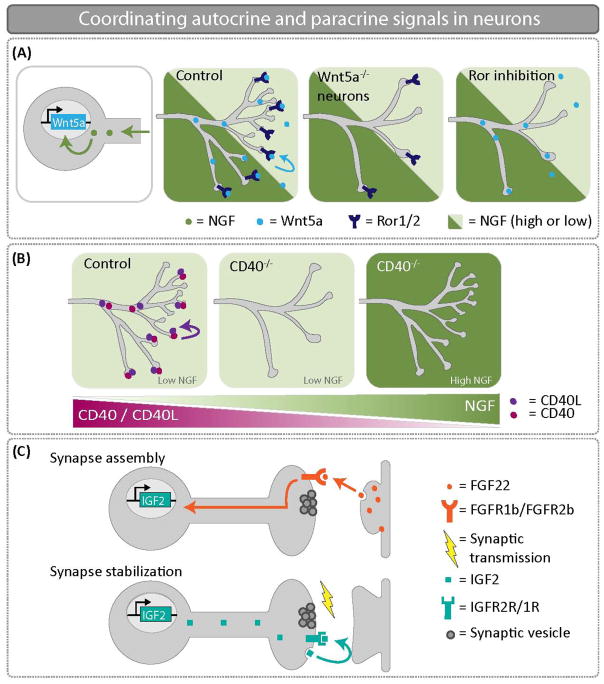
Figure 3.
Coordinating autocrine and paracrine signals in neurons. (A) NGF promotes Wnt5a expression in sympathetic neurons. An autocrine Wnt5a-Ror signal is critical to promote axon branching. When Wnt5a is knocked out specifically in sympathetic neurons, there are significant innervation defects at embryonic day 16.5. (B) NGF represses CD40/CD40L expression in sympathetic neurons. Thus, the CD40/CD40L autocrine signaling loop only functions to drive growth and branching in sympathetic neurons where NGF levels are low. In CD40−/− mice at postnatal day 3, low NGF expressing targets are poorly innervated in the absence of CD40/CD40L autocrine signaling. (C) FGF22 is secreted from CA3 dendrites and promotes assembly of the presynaptic DGC terminal. Retrograde transport of FGF22 induces expression of IGF2. Presynaptic localization of IGF2 is necessary for presynaptic stabilization, and IGF2 transport is regulated by activity. Autocrine IGF2 is required to reinforce and stabilize nascent CA3-DGC synapses.