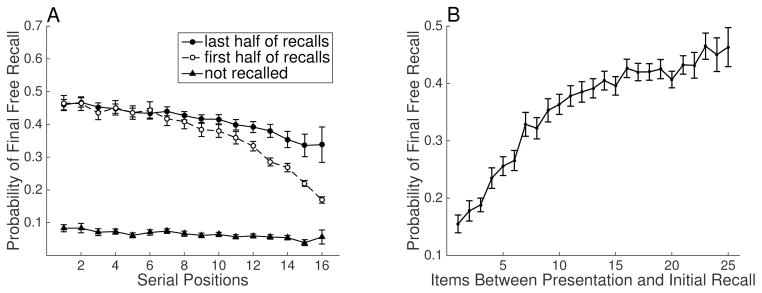
Figure 2. Negative recency in final-free recall. A. Within-list serial position curve.
All 16 lists of Figure 1 are averaged together. The negative-recency effect persists for the first half of recall condition, but is not present for the last half and not recalled conditions. B. Probability of final-free recall as a function of the spacing between initial presentation and recall. As the number of items between the initial presentation and the initial recall of a word increases, the probability of recalling that item during final-free recall increases. Error bars reflect Loftus Masson standard error of the mean.