FIG 8.
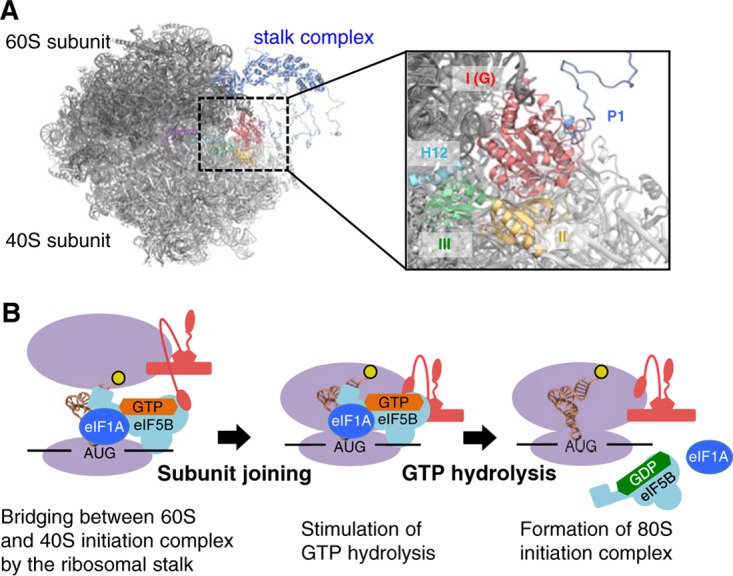
Model of subunit joining in translation initiation. (A) Model of the docking of the aIF5B-GDP-aP1 complex to the 80S initiation complex. The 60S and 40S eukaryotic ribosomal subunits are shown in black and light gray, respectively. The stalk complex, domain I, and domain II of aIF5B are shown in dark blue, red, and yellow, respectively, while domain III, α12 (H12), and domain IV of eIF5B are shown in green, light blue, and purple, respectively. In the docking model, aIF5BI-II-GDP-aP1CTD and the P. horikoshii stalk complex (PDB ID 3A1Y) (12) were superimposed onto the 80S initiation complex with eIF5B (PDB ID 4V8Y) (44), based on the structural alignment for domains I and II of eIF5B and the RNA-binding domain in eukaryotic P0, respectively. The aP0-aP1 stalk complex core and aP1CTD bound to aIF5B-GDP were connected by the flexible hinge region of aP1. Other hinge regions of aP1 were modeled arbitrarily. (B) Schematic representation of the interaction between IF5B and the stalk in the subunit-joining process. The ribosome subunits and the stalk complex are shown in purple and red, respectively. The N-terminal region bound to P0, the hinge region, and the C-terminal region of P1 are modeled as a pentagon, a curved line, and an ellipse, respectively.
