Figure 1.
Pluripotency and Differentiation Capacity of CiPSCs
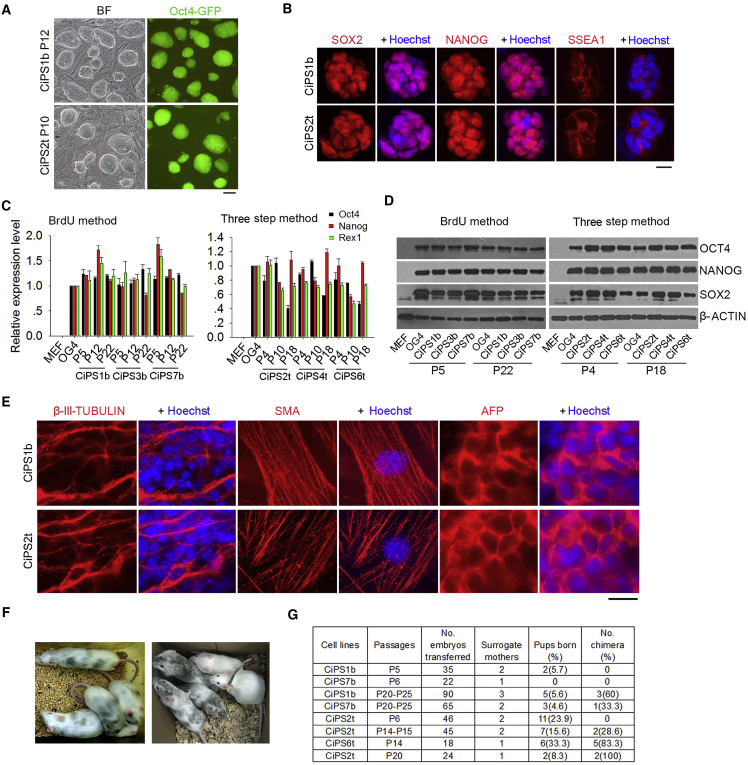
(A) Representative morphology of CiPSCs generated by two methods (BrdU method, CiPSC1b at P12, and three-step method, CiPSC2t at P10) under bright field (BF) with phase contrast optics and expression of Oct4-GFP fluorescence. Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(B) Immunofluorescence microscopy of pluripotent markers SOX2, NANOG, and SSEA1. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(C) mRNA expression levels by qPCR of Oct4, Nanog, and Rex1 in CiPSCs at various passages, compared with isogenic ESCs (OG4) and progenitor MEFs. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.
(D) Protein levels of OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 by western blot analysis of CiPSCs at earlier and advanced passages.
(E) Differentiation capacity in vitro of CiPSCs by immunofluorescence microscopy of three germ layer markers. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(F) Left photo represents chimeras generated from the BrdU method and the right from the three-step method.
(G) Summary table showing percentage of chimeras generated from CiPSCs at different passages compared with OG4 ESCs. Chimeras (black and albino coat) were initially identified by coat color and some confirmed by microsatellite genotyping. CiPSC1b and 7b were generated using the BrdU method and CiPSC2t and the 6t by three-step method.
See also Figure S1.