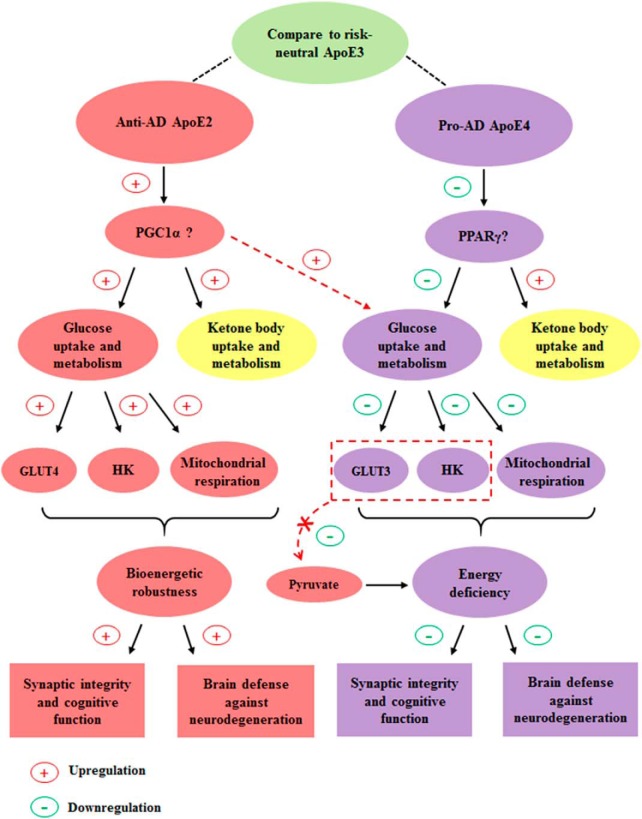
Figure 8.
Our working hypotheses and conclusions. The ApoE2 brain exhibits the most metabolically robust profile, whereas the ApoE4 brain presents the most deficient profile on the uptake and metabolism of glucose, the primary energy source for the brain. Particularly, these two ApoE genotypes are significantly different in the expression of GLUTs and hexokinases. On the uptake and metabolism of ketone bodies, the secondary fuel for the brain, both ApoE2 and ApoE4 brains show more robust profiles than the ApoE3 brain. PGC-1α may serve as an upstream master regulator of the bioenergetic robustness of ApoE2 whereas an inhibition of PPARγ signaling pathway may underlie the energy deficiency associated with ApoE4. In support of this notion, PGC-1α overexpression attenuated the bioenergetic deficits induced by ApoE4. A therapeutic approach that can bypass the deficiency in glucose uptake and glycolysis by providing glucose metabolizing intermediates, e.g., pyruvate, may hold the promise to reduce AD risk in ApoE4 carriers; however, a ketogenic strategy may provide a more meaningful benefit in ApoE3 than in ApoE4 carriers.