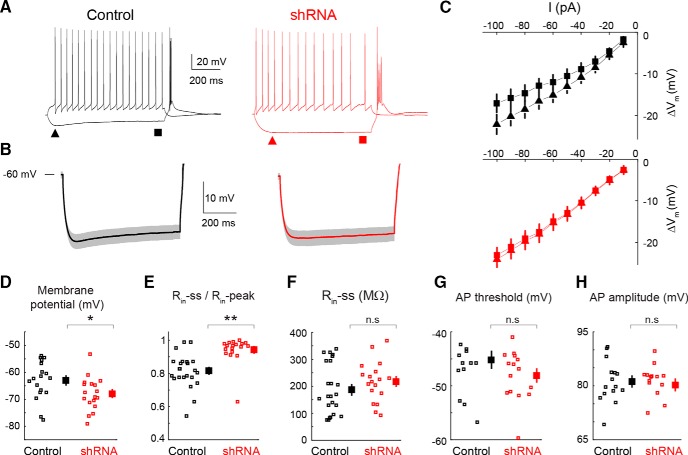
Figure 5.
Effect of the HCN-targeting shRNA on the membrane properties of VB TC neurons in vitro. A, Representative voltage responses of VB TC neurons to a hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current step (−100 and 50 pA, respectively) from nontargeting (black traces, control) and HCN-targeting shRNA-injected (red traces, shRNA) mice (membrane potential, −60 mV for both). Triangles and squares indicate the time of measurement of peak and steady-state input resistance (Rin-peak and Rin-ss, respectively, in the other panels). Note the lack of a depolarizing sag in the hyperpolarizing response of the HCN-targeting shRNA-injected neuron. B, Averaged hyperpolarizing voltage responses (solid line, mean; shadow, ±SEM) in all recorded neurons show the marked reduction in the depolarizing sag in neurons injected with HCN-targeting shRNA (n = 18) compared with control (n = 18). C, Voltage–current plots from all neurons show the lack of inward rectification in HCN-targeting shRNA-injected mice (triangles and squares indicate amplitude of hyperpolarizing pulse at peak and steady state, respectively, compare A, B). D–H, Resting membrane potential (D), ratio of Rin-ss and Rin-peak (E), Rin-ss (F), and action potential (AP) threshold (G) and amplitude (H) for neurons treated with nontargeting (black squares, control) and HCN-targeting shRNA (red squares, shRNA; large symbols indicate mean ± SEM; * and ** indicate statistical significance; n.s., not significant; p values are 0.032 (D), 6.2 10−5 (E), 0.56 (F), 0.17 (G), and 0.44 (H); Wilcoxon rank-sum test).