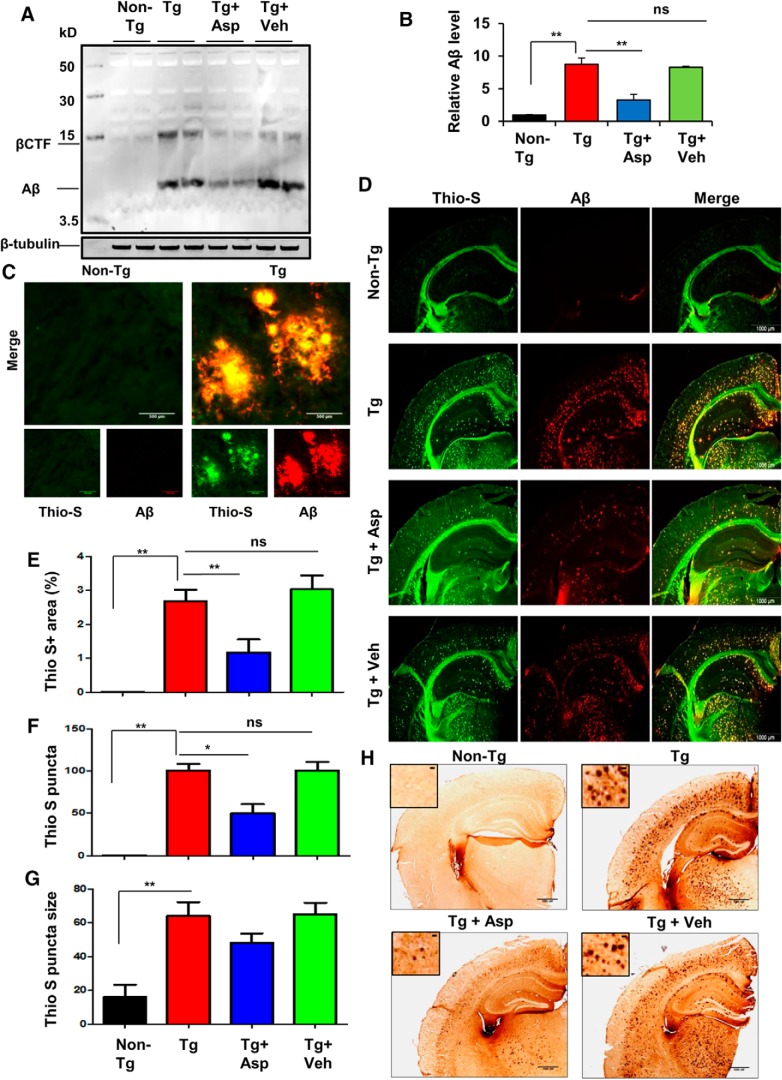
Figure 7.
Aspirin treatment reduces Aβ burden in the hippocampus of a 5XFAD mouse model of AD. A, Six- to 7-month-old 5XFAD mice (n = 6 per group) were treated orally with aspirin (2 mg/ kg body weight/d) or vehicle (0.1% methylcellulose) for 1 month and subsequently analyzed for Aβ levels in the hippocampal homogenates by immunoblotting using the 4G8 monoclonal antibody. β-Tubulin was used as the loading control. B, Densitometric analysis representing mean ± SEM for Aβ levels relative to non-Tg controls. C, Hippocampal sections demonstrating Aβ plaque pathology in transgenic 5XFAD mice in the CA1 region of hippocampus. D, Hhippocampal sections were double labeled using thio-S and Aβ 6E10 antibody. E–G, The thio-S-positive plaques in the hippocampus were further characterized for total area faction (thio-S positive area as a percentage of total hippocampal area; E), plaque count (F), and average plaque size (G). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Quantification of thio-S-positive plaques were performed using ImageJ. H, Diaminobenzidine staining of hippocampal sections was performed using Aβ 6E10 antibody. In all cases, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparisons test was used for statistical analysis; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001.