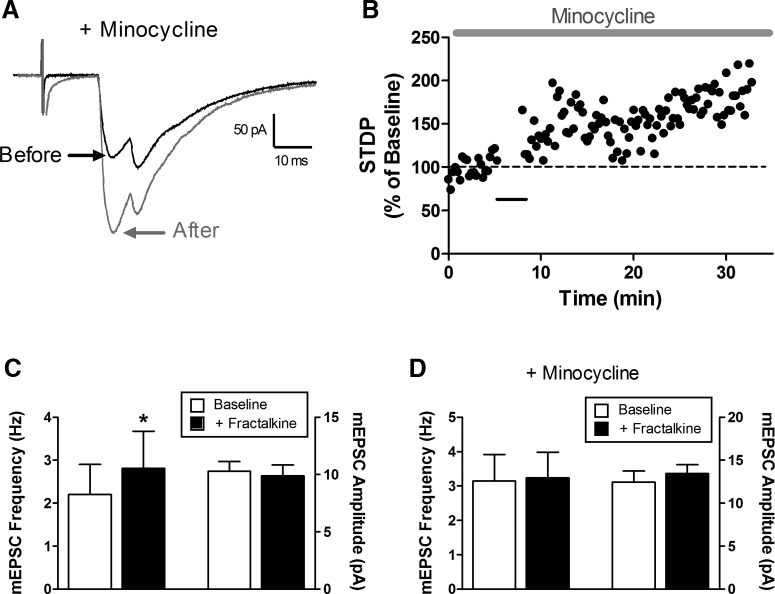
Figure 8.
Minocycline fails to prevent t-LTP at primary afferent synapses onto spino-parabrachial neurons. A, Representative primary afferent-evoked EPSCs before (black) and after (gray) the administration of the t-LTP pairing protocol in the presence of minocycline to prevent microglial activation. B, Current versus time plot demonstrating a significant potentiation in EPSC amplitude following the administration of the t-LTP pairing protocol (black bar) in the continued presence of minocycline. C, Bath application of the CX3CR1 ligand fractalkine significantly increased mEPSC frequency in lamina I neurons (*p = 0.031; Wilcoxon signed-rank test; left) without influencing mEPSC amplitude (p = 0.562; right). D, Minocycline blocked the fractalkine-evoked increase in mEPSC frequency within lamina I (p = 1.0; Wilcoxon signed-rank test; left).