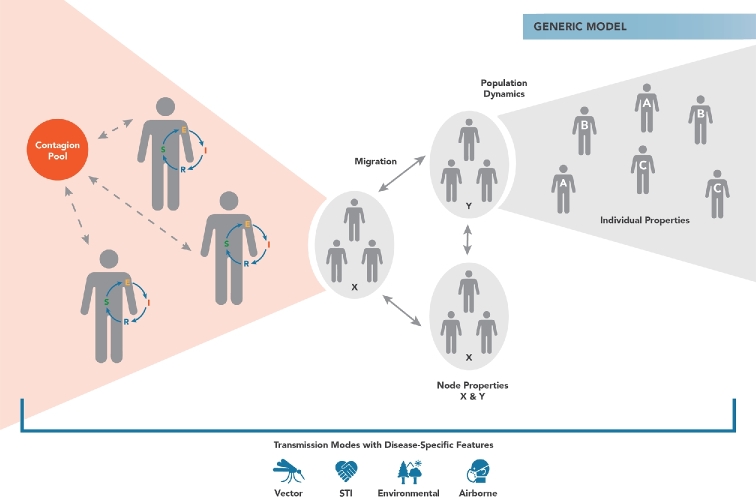
Figure 1.
Diagram of the Generic transmission model in EMOD, in which the within-host disease process is represented as progression through the states of susceptible (S), Exposed (E), Infected (I) and Recovered (R). The dynamics of a compartmental SEIRS model can be produced when infected individuals shed infectiousness into a shared contagion pool (red circle) and susceptible individuals acquire from this pool. The Generic model allows for multiple contagion pools to be created based on geographic location (node) and modified based on the properties of the node. EMOD allows for individuals to have differential shedding and exposure according to demographic strata, including user-defined strata called individual properties. By representing SEIRS as internal states of the individual rather than compartments of the population, EMOD allows the transmission mode to be modified—for example, to a relationship network for sexual transmission—while the individual disease progression continues to follow the same SEIRS states.