Fig. 1.
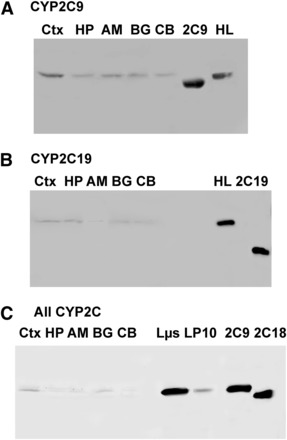
CYP2C protein expression in human brain microsomes. (A–C) Affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies raised against CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and recombinant CYP2C18 (“All CYP2C”) were used to assess CYP2C9 (A), CYP2C19 (B), and total CYP2C expression (C) in the cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia, amygdala, and cerebellum. For CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 blots, 20 μg protein pooled from the three samples described in Supplemental Table 2 were loaded in each lane. For the blot incubated with the all-2C antibody, 10 μg protein was loaded from one representative brain sample. Recombinant proteins used as standards in (A) and (B) contained truncated N-terminal peptide sequences compared with the full-length, native proteins in liver and brain fractions. Recombinant CYP2C9 and CYP2C18 in (C) were expressed from full-length constructs (Cuttle et al., 2000; Shukla et al., 2005). 2C9, recombinant CYP2C9; 2C18, recombinant CYP2C18; 2C19, recombinant CYP2C19; AM, amygdala; BG, basal ganglia; CB, cerebellum; CTX, cortex; HL, human liver microsome; HP, hippocampus; Lµs, human liver pellet microsomal fraction from centrifugation at 110,000 × g; LP10, human liver pellet fraction from centrifugation at 110,000 × g.
