Fig. 4.
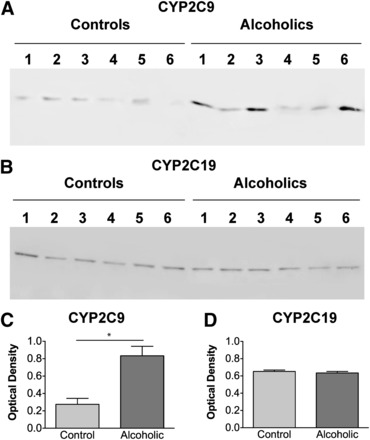
(A and B) Immunoblot of microsomal fractions (pellets from centrifugation at 110,000 × g) of the frontal cortex of six individual control and six individual alcoholic case-matched human brain samples using antibodies detecting CYP2C9 (A) and CYP2C19 (B). An equivalent amount (20 μg) of total protein was loaded in each lane. (C) Individual sample densities were corrected against beta-actin and the corrected data were subjected to a t test with a 95% confidence interval. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. The asterisk indicates that CYP2C9 expression in samples from alcoholics was significantly elevated over expression in controls (n = 6; P < 0.05, 95% confidence interval). No significant differences were seen in CYP2C19 expression between samples from alcoholics and controls.
