Figure 1.
Two Subtypes of Clones Exist in an hPSC Population
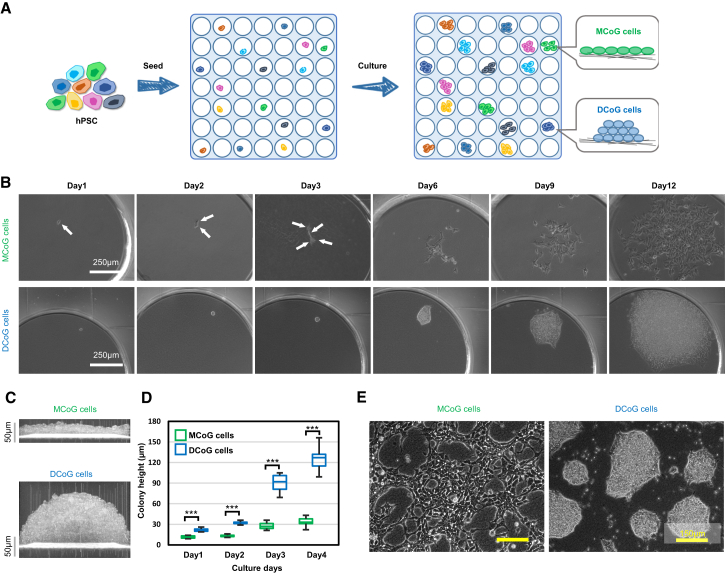
(A) Schematic representation of single-cell dissociation and culture strategy. In the following figures, green represents MCoG cells and blue represents DCoG cells.
(B) Single hPSCs grew into multicellular clones during the culture course from day 1 to 12. These clones demonstrated two types of morphologies: flat monolayer cells (top panel) and domed-multilayer cells (bottom panel). To prevent single-cell apoptosis, ROCK inhibitor (10 μM) was added on the first 5 days and removed from day 6. White arrows indicate the individual cells.
(C) Cross-section images of colonies of two types of cells were observed by optical coherence tomography (OCT) microscopy system in real time.
(D) The colony height of MCoG and DCoG cells on culture days 1, 2, 3, and 4 (ROCK inhibitor was removed from day 2) (mean ± SD, n = 10 independent biological replicates, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). Colonies height were measured by OCT microscopy system.
(E) The bright-field images of two types of clones after 27 passages on GNF substrate, showing maintained morphologies, respectively.
See also Figures S1 and S2.