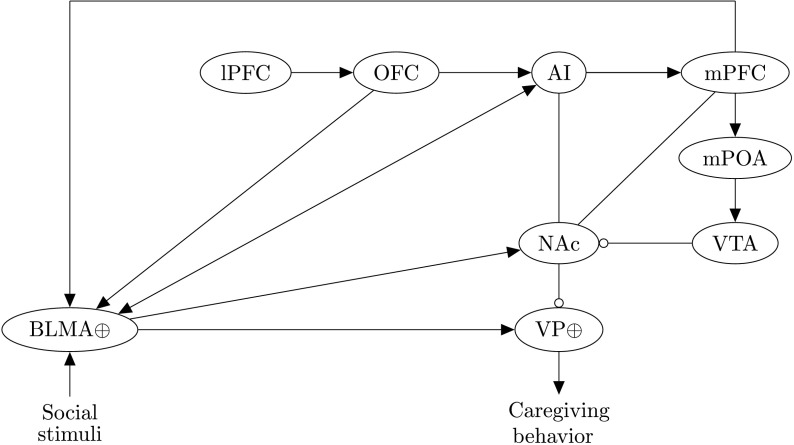
Figure 2. .
Numan’s neuroanatomical model for how empathic states can motivate caregiving behavior. Stimuli enter the BLMA, which projects to the AI to create an empathic state and to the NAc and VP to drive caregiving behavior. The AI projects to the medial prefrontal cortex (including the anterior cingulate), which is proposed to activate a mesolimbic caregiving pathway from the mPOA to the VTA and the NAc, inhibition of which releases the VP from NAc inhibition mediated via BLMA inputs. Projections from lPFC and OFC cortices to the AI and BLMA are additional pathways that can potentiate the caregiving response, as are projections from AI and mPFC to the NAc. Ellipses represent neural populations, arrows are excitatory synapses, and circles are inhibitory synapses (the nature of the connections between AI and NAc and between mPFC and NAc within this context is currently unknown). ⊕ denotes positively valent neurons (i.e., populations that subsequently activate prosocial/approach pathways). From Numan (2014, p. 278). Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.