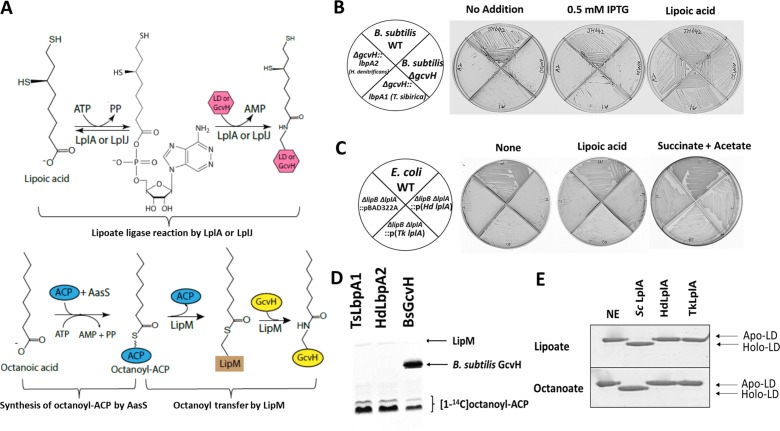
Figure 6. In vivo and in vitro activities of lbpA and LbpA.
(A) Biochemical reactions for lipoate/octanoate assembly. Upper panel, lipoate ligase reaction catalyzed by LplA or LplJ. When lipoic acid is provided in the environment, LplA/LplJ catalyzes the ligase reaction in two steps. First, lipoic acid is activated to lipoyl-AMP with concomitant release of pyrophosphate. In the presence of a LD or GcvH acceptor protein, the lipoyl moiety is transferred to the LD or GcvH. LD, lipoyl domain. Lower panel, synthesis of octanoyl-ACP and amidotransfer of octanoyl moiety from ACP to GcvH. The synthesis of octanoyl-ACP requires AasS (the acyl-ACP synthetase from Vibrio harveyi) holo-ACP, ATP and free octanoic acid. The octanoyl transfer step requires LipM, which is the octanoyl transferase in B. subtilis. (B) Complementation of B. subtilis ∆gcvH NM20 strain with lbpA genes from sulfur oxidizers and LipM modification assay. The lbpA genes were integrated into the chromosomal amyE site of the B. subtilis ΔgcvH strain under control of Pspac promoter and were inducible by IPTG. Colony formation was scored on minimal agar plates with glucose as the sole carbon source and supplements indicated after 36 hr at 37°C. The wild type (JH642) and B. subtilis ∆gcvH strain (NM20) served as positive and negative controls, respectively. No discrete colonies were formed by the strains that expressed LbpA1 and LbpA2 (the imperfections are scratches from the streaking), whereas strains all grew well with lipoic acid supplementation. (C) Complementation of lipoate auxotrophic E. coli ∆lipB ∆lplA strain with LplA proteins from sulfur oxidizers. The control strains were the wild-type (WT) strain and E. coli ∆lipB ∆lplA strain containing the empty vector (pBAD22A). Strains were grown on M9 minimum glycerol media plates with the indicated supplements at 37°C for 36 hr. Complementation proceeded both in the presence and absence of arabinose induction. Plates above contained 0.2% arabinose. (D) Assay of [1-14C]octanoyl transfer from [1-14C]octanoyl-ACP to lipoate-binding proteins (TsLbpA1 from T. sibirica and HdLbpA2 from H. denitrificans) and to B. subtilis GcvH (BsGcvH) as indicated in the figure. The [1-14C]octanoyl-ACP was synthesized in situ by Vibrio harveyi AasS acyl-ACP synthetase (ATP was added for the AasS reaction). Reaction was analyzed on SDS-PAGE by autoradiography. (E) Mobility shift assay for analysis of in vitro lipoylation and octanoylation catalyzed by LplA using the E2AceF E. coli lipoyl domain (LD) as acceptor. Loss of the positive charge of the modified lysineε−amino group of the LD results in faster migration of the modified form on Urea-PAGE gels. NE, no enzyme; Sc LplA, LplA from S. coelicolor; HdLplA, LplA from H. denitrificans; TkLplA, LplA from Thioalkalivibrio sp. K90mix.