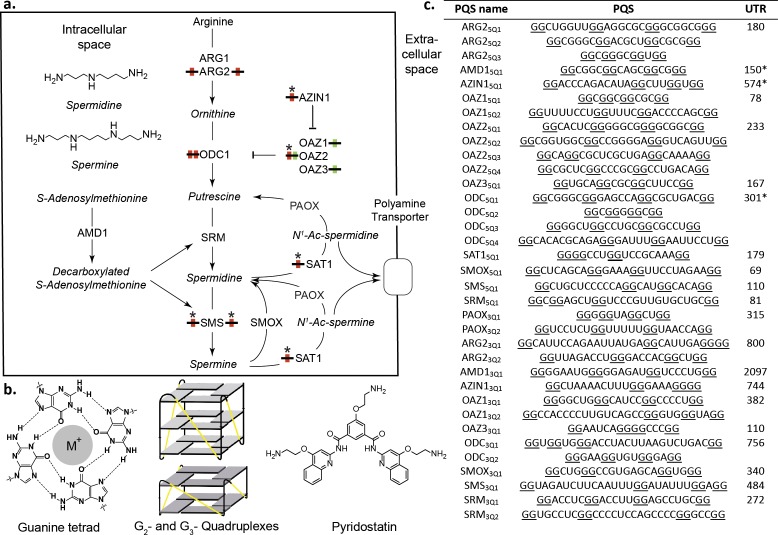
Figure 1. Polyamines (PAs) and G-quadruplexes.
(a) PA biosynthesis pathway and summary of the roles/regulation of putative quadruplex sequences (PQS’s) on PA biosynthesis. Red: G2-rich motifs inhibit PA biosynthesis; Green: G2-rich motifs enhance PA biosynthesis; *: PA-sensing G2-rich motifs. (b) Guanine tetrad stabilized by a monovalent cation (M+) and intramolecular parallel G2- and G3-quadruplexes. Quadruplex loops - yellow. (c) G2-rich motifs in the UTRs of PSPs. PQS’s are denoted as the gene name with the UTR and PQS number (Qn; where n=≥1). Underlined guanines are those forming the most stable predicted G2-PQS from all possible PQS’s predicted by QGRS Mapper (version: Feb. 2014). Full length UTRs were utilized in the study in all cases except for the 5 UTRs of AMD1, AZIN1 and ODC1. *portion of the UTR used in this study for AMD1, AZIN1 and ODC1 (AMD1: 150-AUG; AZIN1: 720-241 and 95-AUG; ODC1: 301-AUG) (See Supplementary file 1 and Supplementary file 2 for details). ARG1, ARG2: arginase 1-2; ODC1: ornithine decarboxylase; SRM: spermidine synthase; SMS spermine synthase; AMD1: adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1; AZIN1: antizyme Inhibitor 1; OAZ1-3: ornithine decarboxylase antizyme 1-3; SAT1: spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1; SMOX: spermine oxidase; PAOX: polyamine oxidase.