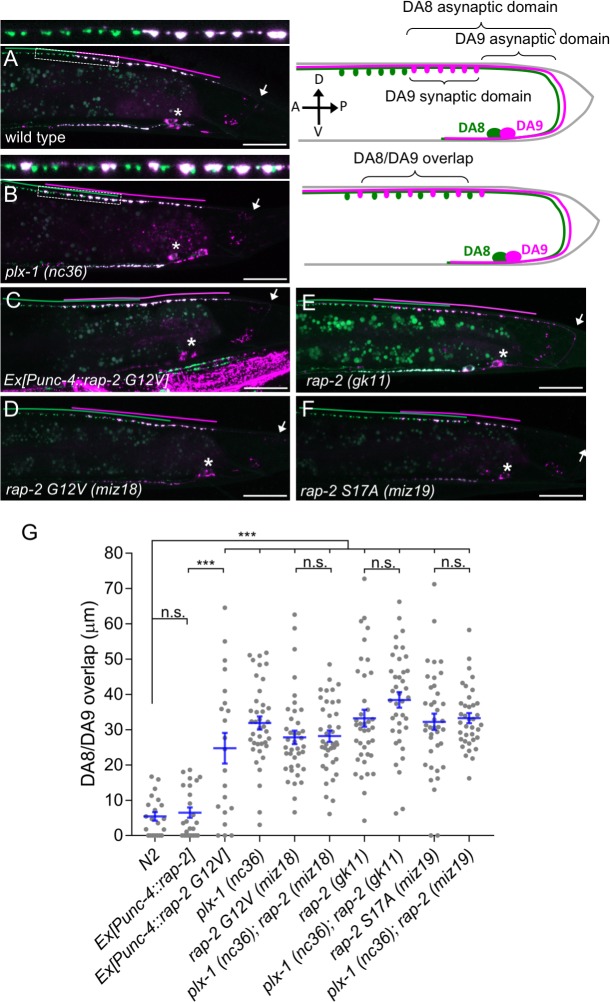
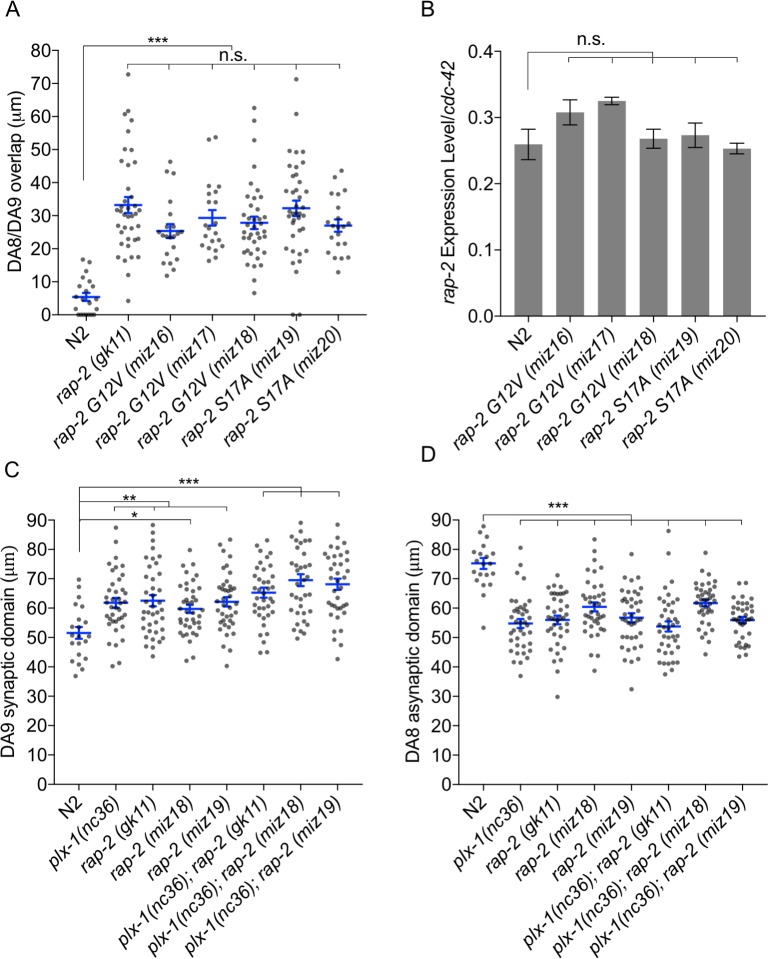
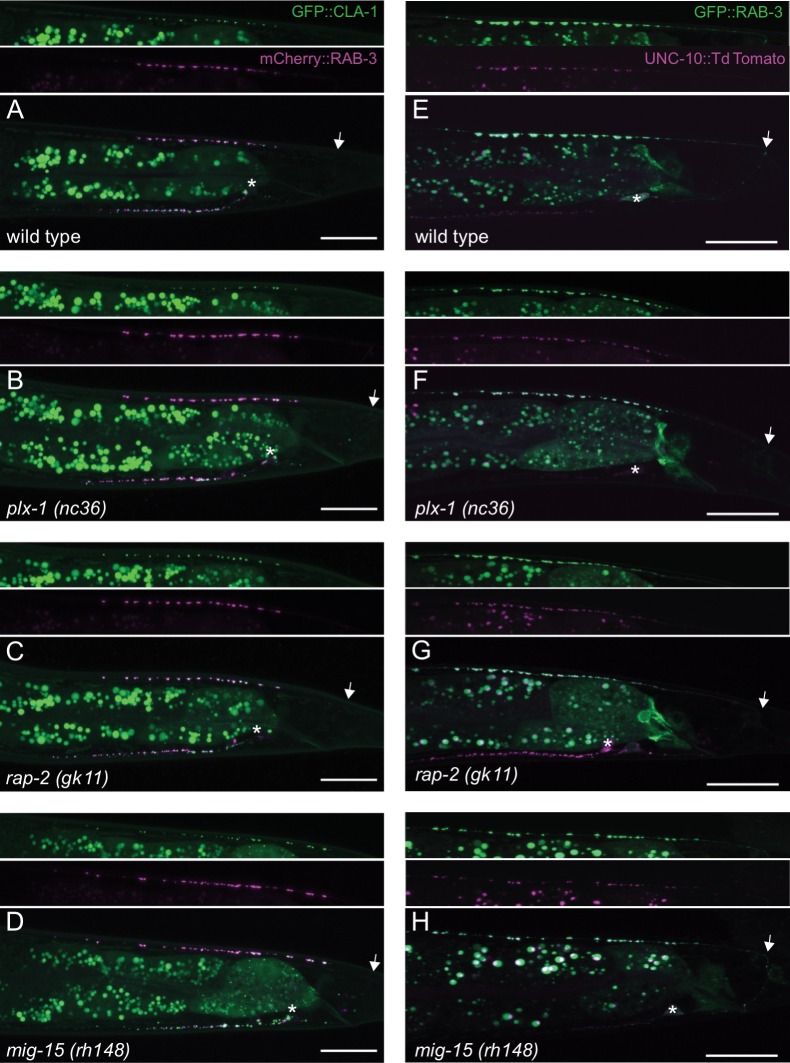
Figure 1. Gain- and loss-of-function rap-2 mutants show synaptic tiling defects.
(A and B) Representative image of synaptic tiling of wild type (A) and plx-1 mutant (B) animals. Images show wyIs446 marker to label synapses in DA8 (GFP::RAB-3) and DA9 (GFP::RAB-3+mCherry::RAB-3). Dotted box represents the magnified images from A and B of the synaptic tiling border. Schematics of DA8 (green) and DA9 (magenta) neurons with parameters for analysis shown on the right. (C–F) Representative images of wyIs446 strains with the following genotypes: rap-2(G12V) overexpression in DA neurons (C), rap-2 G12V (miz18) (D), rap-2 null (gk11) (E) and rap-2 S17A (miz19) (F). Synaptic domains from DA8 and DA9 are highlighted with green and magenta lines, respectively. Asterisks: DA9 cell body. Arrows: dorsal commissure of DA9. Scale bars: 20 μm. (G) Quantification of overlap between DA8 and DA9 synaptic domains. Each dot represents a single animal. Blue bars indicate mean ± SEM. n.s.: not significant; ***p<0.001.