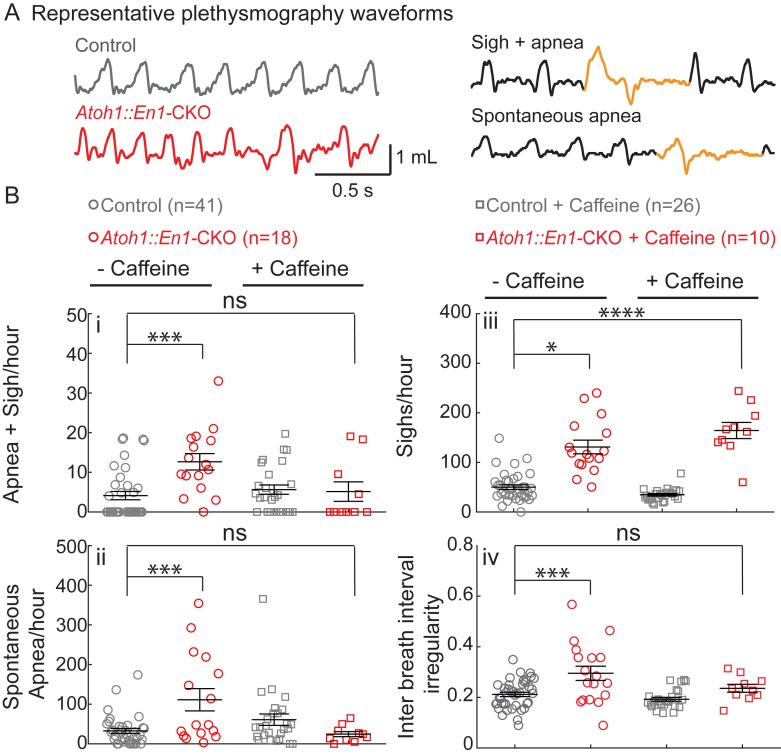
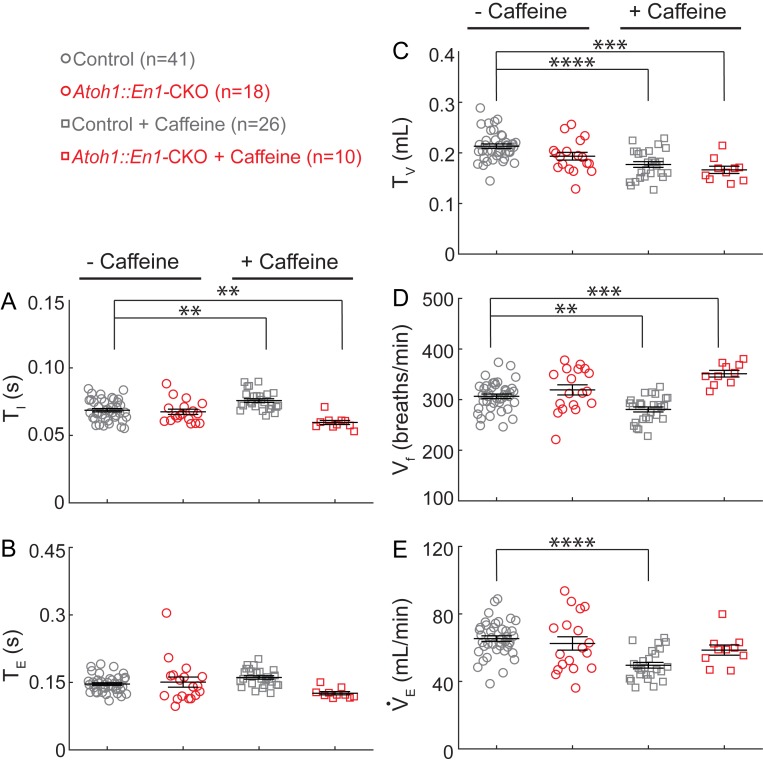
Figure 2. Atoh1::En1-CKO mice have many apneas causing irregular breathing rhythms that can be rescued by caffeine treatment in room air.
(A) Representative plethysmography traces from a control and Atoh1::En1-CKO mouse. Example traces of apnea and sigh. (Bi) Atoh1::En1-CKO mice have more apneas following sighs and (Bii) spontaneous apneas per hour than control littermates. Caffeine treatment rescues apneas. (Biii) Atoh1::En1-CKO mice have more sighs per hour than control littermates, which was not be rescued by caffeine. (Biv) Atoh1::En1-CKO mice breathe more irregularly than control littermates, which can be rescued with caffeine treatment. Inter breath interval irregularity was defined as: absolute (breath length(n + 1) – breath length(n)/breath length(n). Significance was determined using a Two-way ANOVA (genotype*treatment), Tukey-Kramer post-hoc. *p<0.05. **p<0.01. ***p<0.001. ****p<0.0001. Error bars represent: mean ± SEM.