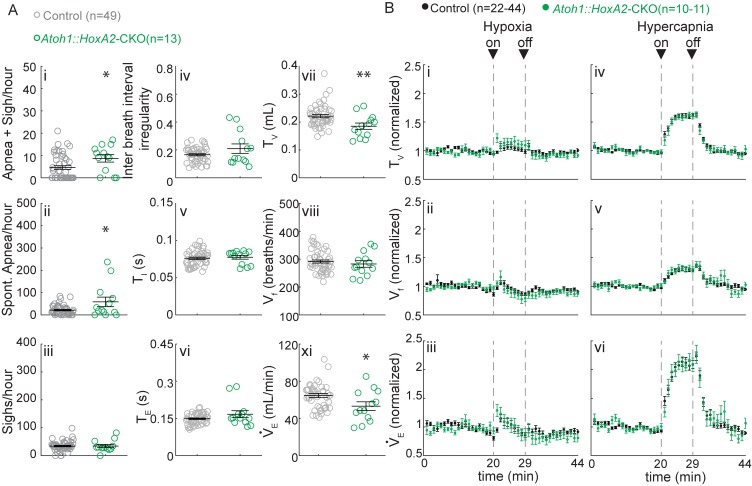
Figure 6. Atoh1::HoxA2-CKO mice have normal chemoresponses.
(A) Atoh1::HoxA2-CKO mice have more apneas following sighs (i) and spontaneous apneas (ii) than control littermates and a smaller tidal volume per breath (TV) (vi) resulting in smaller minute ventilation (VE) (Viii). Other breathing parameters were not affected. Significance for room air breathing parameters were determined using a t-test (2-tailed). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (B) Atoh1::HoxA2-CKO mice have normal respiratory chemoresponses in hypoxia (i to iii) and hypercapnia (iv to vi). Significance was determined using a t-test (2-tailed) at each individual time point, *p<0.0011 (0.05/44 for Bonferroni correction). Error bars represent mean ± SEM.