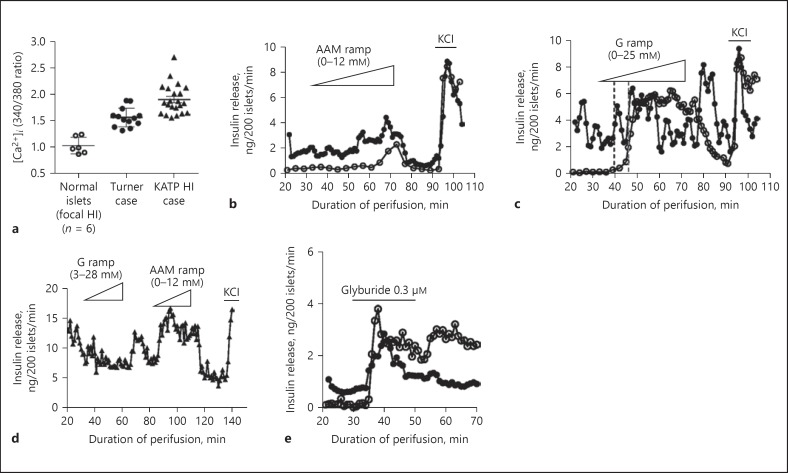
Fig. 3.
Functional studies of isolated islets from Turner syndrome case 7. a Basal cytosolic calcium was elevated in islets from case 7 (filled circles) compared to age-matched control islets (n = 6, open circles) and similar to islets from a child with loss of function mutations in the KATP gene ABCC8 (filled triangles). Basal calcium measurements from control islets from 6 individuals are shown as averages while the calcium measurements in islets from 1 Turner syndrome case and 1 KATP hyperinsulinism (HI) case are shown as individual islets. Note that basal insulin secretion was also elevated in islets from case 7 compared to control islets (b, c), similar to the elevation of basal insulin release in islets from a patient with KATP hyperinsulinism (d). b Insulin secretion was stimulated by an amino acid mixture (AAM) in islets from case 7 and was minimal in control islets. c Insulin secretion was stimulated by a glucose (G) ramp in normal islets and in islets from case 7 (dashed lines indicate threshold concentrations for insulin release: 2.5 mM in case 7 vs. 5.6 mM in control islets). d Islets from a child with hyperinsulinism due to compound heterozygous inactivating mutations of ABCC8 (c.2222 + 15c>a and c.1933delG) responded to stimulation with an amino acid mixture (AAM) ramp, but failed to respond to a glucose (G) ramp. e Insulin secretion was stimulated by glyburide, a KATP channel antagonist, in both control islets and in islets from case 7.