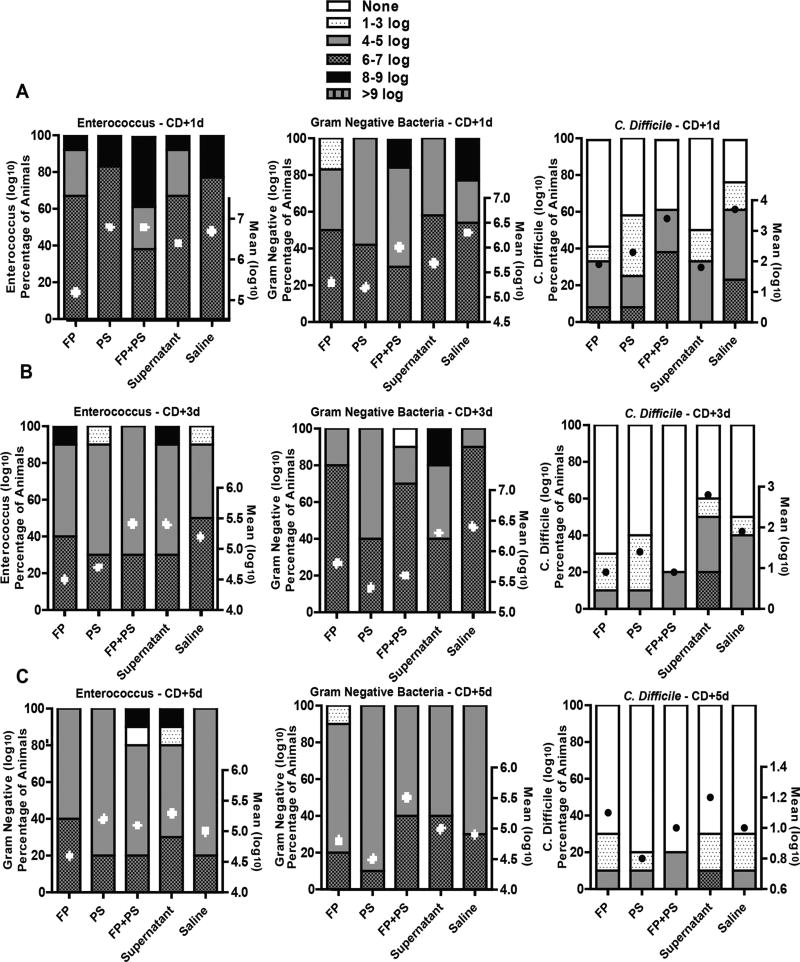
Figure 2.
Bacterial colonization after Clostridium difficile (CD) exposure. Mice were randomized into groups and treated with clindamycin as described in Figure 1. Three days after the last dose of clindamycin, mice were orally exposed to VA17 (4 log10 CFU/mL). Mice received the randomized supplements daily. Concentration of enterococcus, gram-negative bacteria, and CD was measured by plating serially diluted fresh stool samples on selective agar on (A) day 1, (B) day 3, and (C) day 5 after CD challenge. Data are presented as mean log10 CFU/g ± SEM, and percentage of animals in each group with range of log10 CFU/g set as none, 1–3, 4–5, 6–7, 8–9, and >9 log10 CFU/g. n = 10 animals/group. FP, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii; PS, potato starch.