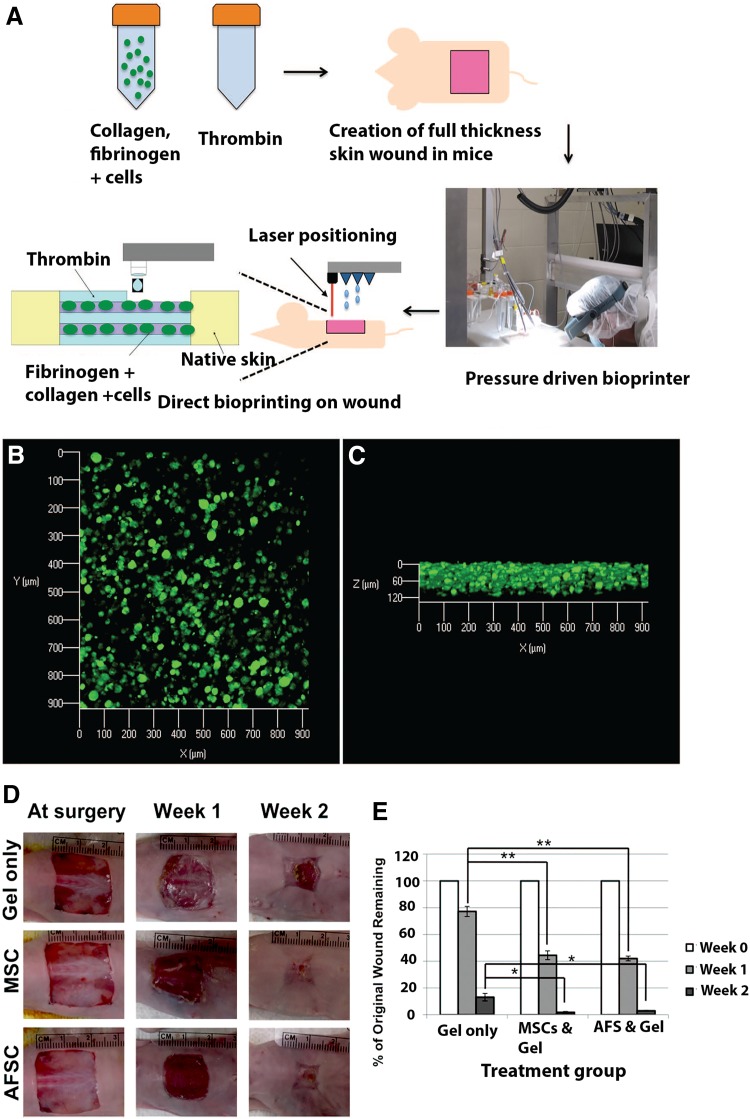
Fig. 2.
Bioprinting of stem cells for the treatment of skin wounds. a: A schematic describes the approach by which amniotic fluid-derived stem cells (AFSC) are bioprinted in order to increase healing of a full-thickness skin wound. Wounds containing the deposited gels with green fluorescent protein-tagged AFSC were harvested after 24 h of post-printing and analyzed with confocal microscopy. Images revealed evenly distributed cells in the gels, as viewed from the top b or from the side (c). d: Gross histology images illustrating wound closure in gel-only, MSC, and AFS treatments. e: Percentage of unhealed wound remaining at the day of surgery, after one and 2 weeks. Abbreviations: AFS amniotic fluid-derived stem cells, AFSC amniotic fluid-derived stem cell, MSC mesenchymal stem cell. Adopted with permission from (Skardal et al. 2012)