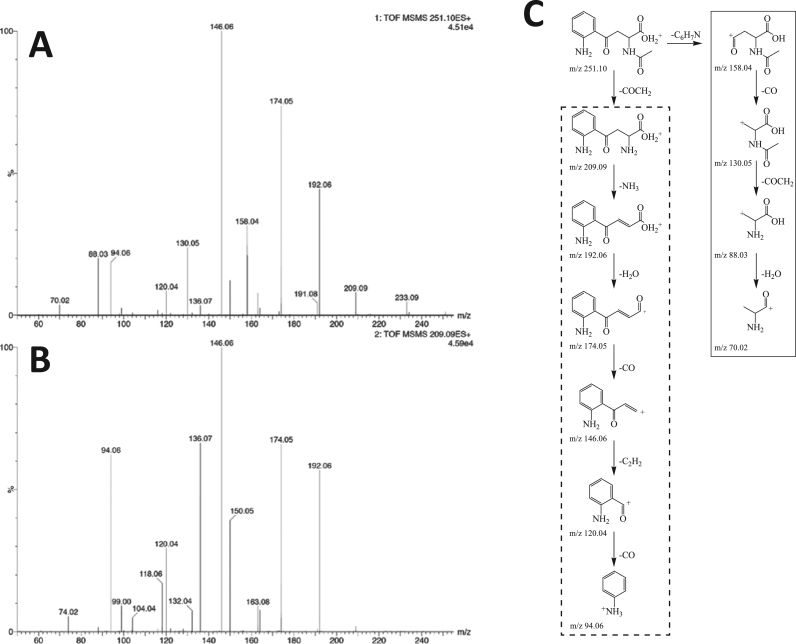
Fig. 1.
LCMS-MS spectra of NAK ([M+] = 251.10) (A) identified in LMWF5A and synthetic KYN ([M+] = 209.09) in saline (B). Structural similarities include mass fragments at m/z 192.06, 174.05, 146.06, 120.04, and 94.06. Structural differences include mass fragments at m/z 158.04, 130.05, 88.03, and 70.02 seen in the NAK spectrum only. (C) Proposed fragment structures for the observed product ions using the LCMS-MS conditions listed in the Materials and Methods section. The structural similarities of NAK ([M+] = 251.10) and KYN ([M+] = 209.09) include mass fragments at m/z 192.06, 174.05, 146.06, 120.04, and 94.06 (dotted box). The structural differences of NAK and KYN include mass fragments at m/z 158.04, 130.05, 88.03, and 70.02 (solid box). A synthetic standard of NAK was analyzed by LCMS and shown to be structurally identical to [M+ ] = 251.10 identified in LMWF5A (data not shown).