Figure 1.
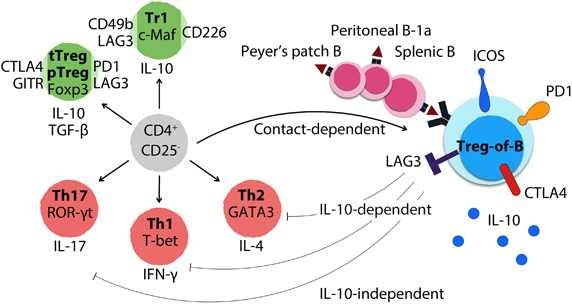
B-cell-induced CD4+Foxp3− regulatory T cells. When exposed to B cells from the spleen and Peyer’s patch, as well as B-1a cells from the peritoneal cavity, CD4+CD25− T cells are triggered to differentiate into CD4+CD25+Foxp3− regulatory T cells dependent on cell–cell contact. These B-cell-induced Treg cells are named Treg-of-B cells, which express both regulatory T-cell-related molecules, such as ICOS, PD1, OX40, LAG3 and CTLA4, and inhibitory cytokines, such as IL-10 and TGF-β. Treg-of-B cells express lower or no master transcription factors of thymus-derived Treg, Tr1, Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells. Treg-of-B cells exert antigen-specific and non-antigen-specific suppressive functions in IL-10-dependent, IL-10-independent and cell contact-dependent manners. Notably, prophylactic transfer of Treg-of-B cells prevents Th2-dominant allergic asthma, Th1/Th17-mediated inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis in mice.
