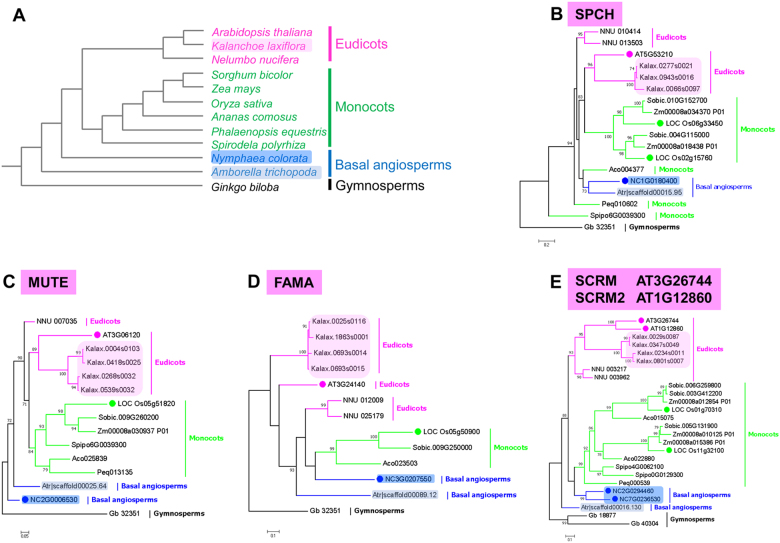
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic trees of stomatal bHLH genes in representative species.
a The molecular tree summarizes the phylogenetic relationships of representative species, including gymnosperms (e.g., Ginkgo biloba), basal angiosperms (e.g., Amborella trichopoda and Nymphaea colorata), monocots (e.g., Oryza sativa and Spirodela polyrhiza), and eudicots (e.g., Arabidopsis thaliana and Kalanchoe laxiflora). b-e Gene trees of master regulatory bHLH transcription factors SPCH (b), MUTE (c), FAMA (d) and ICE1/2 (e) in stomatal development. Amino-acid sequences from G. biloba (Gb), A. trichopoda (Atr, grey shade), N. colorata (Nc, blue shade), S. polyrhiza (Spipo), Phalaenopsis equestris (Peq), Zea mays (Zm), O. sativa (Loc_Os, green circle), Nelumbo nucifera (NNU), K. laxiflora (Kalax, peachy shade) and A. thaliana (AT, peachy circle) were used to generate trees