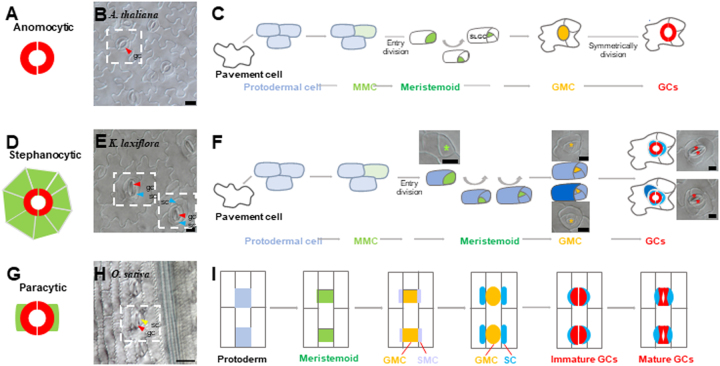
Fig. 7. Mature stomatal types and development in diverse species.
a, d, g Mature stomatal types. Diagrams show the guard cell pair (red) and subsidiary cells (green). a Anomocytic stomata lack subsidiary cells. d Stephanocytic stomata possess a ring of subsidiary cells. g Paracytic stomata possess one pair of lateral subsidiary cells oriented parallel to the guard cells. b, c Example of eudicot stomata in A. thaliana. b The upper epidermis of A. thaliana with anomocytic stomata. c Schematic diagram of stomatal development transitions. A subset of protodermal cells (pale blue) enter the stomatal lineage and take on an MMC identity; the MMC (pale green) undergoes asymmetric cell division producing a smaller meristemoid (green) and larger SLGCs (white). Then, the meristemoid differentiates into a GMC (orange), and the GMC undergoes a symmetric division to form a pair of guard cells (red). e, f Example of eudicot stomata in K. laxiflora. e The upper epidermis of K. laxiflora with stephanocytic stomata. f Schematic diagram of stomatal development. Protodermal cells (pale blue) take on an MMC identity. The MMC (pale green) divides through three or four asymmetric divisions to give rise to a GMC (orange), and a round of neighbouring cells (dark blue) eventually become subsidiary cells (blue) surrounding the guard cells (red). h, i Example of monocot stomata in O. sativa. h The upper epidermis of O. sativa with linear cell files and paracytic stomata. i Diagrams illustrating stomatal development for the stomatal complex. Cell protoderm files (pale blue) asymmetrically divide to create a meristemoid (green), and the meristemoid differentiates into a GMC (orange). Then, neighbouring cell files (SMC, pale purple) divide asymmetrically to form SCs (blue). Finally, the GMC divides once symmetrically to form GCs (red), and the GCs and SCs terminally differentiate and form mature dumbbell-shaped stomata. Key: protodermal cell that will give rise to the stomatal lineage, pale blue; MMC (meristemoid mother cell), pale green; meristemoid, green; SLGCs (stomatal-lineage ground cell), white; GMC (guard mother cell), orange; GCs (guard cells), red; SMC (subsidiary mother cell), pale purple; SCs (subsidiary cells), blue