Figure 4.
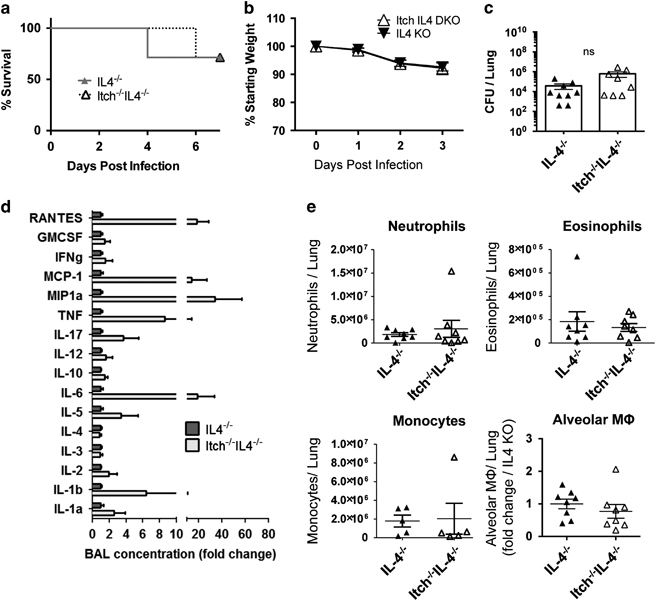
Itch−/−IL-4−/− mice exhibit comparable bacterial control and alveolar macrophages as IL-4−/− control mice. IL4−/− and Itch−/−IL4−/− mice were infected intranasally with 103 CFU K. pneumoniae. (a) Survival (n=7–8, combined from two independent experiments), (b) Weight loss (n=10–11) and (c) bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) in lung homogenate on day 3 post infection (n=8, compiled from three independent experiments). (d) BAL cytokines were quantified using the Quansys 16-cytokine enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay array (n=6, compiled from three independent experiments). (e) Myeloid cells were identified from lung single-cell suspensions using flow cytometry. Neutrophils were CD45+SiglecF−CD11b+Ly6G+, eosinophils were CD45+SiglecF+CD11c−, monocytes were CD45+, SiglecF−, Ly6G−CD11b+Ly6C+ and alveolar macrophages were CD45+CD11c+CD11bloSiglecF+ (n=5–8, compiled from three independent experiments). Dots represent individual mice. Significance was determined for survival, weight loss and cytokine/bacterial burden/myeloid cell populations as follows: Log-rank test, two-way analysis of variance and unpaired t-test were used, respectively.
