Figure 5.
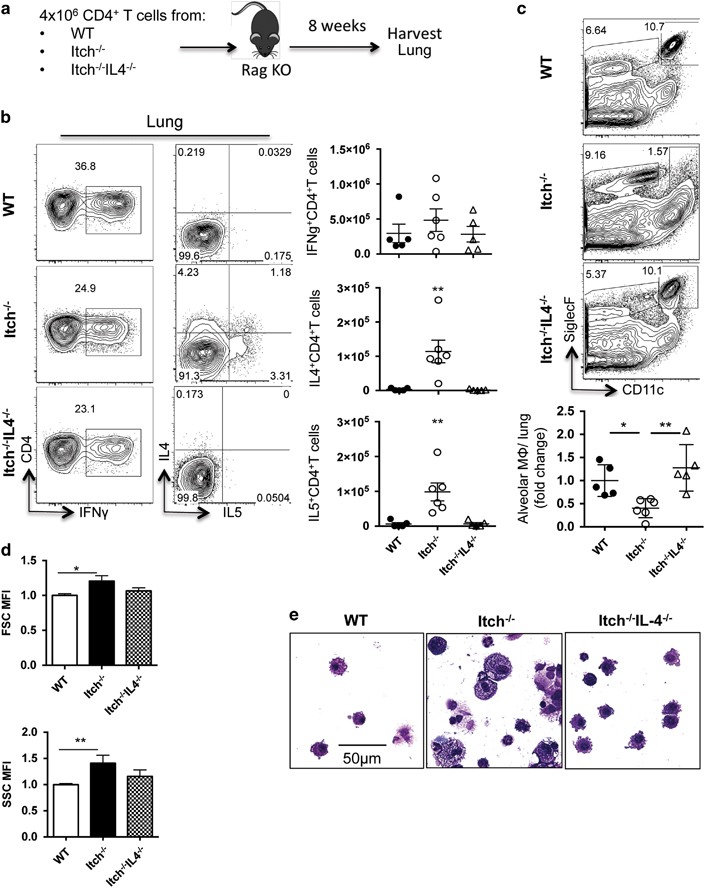
Itch−/− CD4+ T cells are sufficient to drive loss of alveolar macrophages in an IL-4-dependent manner. (a) Diagram describing experimental design. A total of 4 × 106 purified spleen CD4+ T cells from WT, Itch−/− or Itch−/−IL4−/− mice were transferred intravenously to Rag−/− mice, then BAL and lungs were collected 8 weeks later. (b) Lung cell suspensions were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 4 h in the presence of Brefeldin A, and then cells were stained for surface markers and intracellular cytokines. Representative flow cytometry plots and quantifications of absolute numbers are shown. Cells are gated on live, singlet, CD3+CD4+. Dots represent individual mice (n=5–6). (c) Alveolar macrophages were identified from lung cell suspensions by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry plots and quantification of alveolar macrophages are shown. Flow plots were gated on live, singlet, CD45+, and alveolar macrophages were CD11c+CD11bloSiglecF+. (d) The mean fluorescence intensity of the forward- and side-scatter parameters (FSC and SSC, respectively) was calculated for alveolar macrophages using the geometric mean formula on FlowJo software. Alveolar macrophage numbers, FSC and SSC were divided by the average WT numbers within each experiment to calculate fold change per experiment, normalizing for experimental variability (n=5–6, compiled from two independent experiments). (e) Representative BAL cytospins stained with modified Giemsa stain and visualized at × 40. Significance was calculated using a one-way analysis of variance. * or ** denote P≤0.05 or P≤0.01, respectively.
