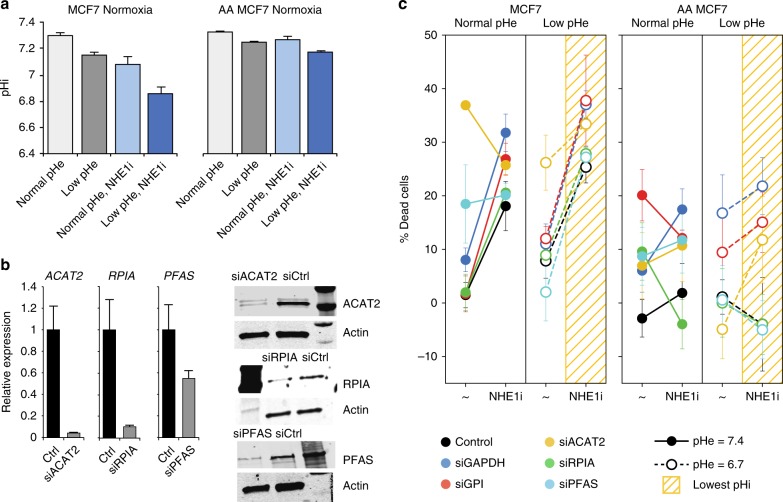
Fig. 4.
Validation of systems analyses in predicting pHi-sensitive metabolic vulnerabilities. a pHi measurements of naïve and acid-adapted (AA) breast cancer MCF7 cells, under normoxia and following the inhibition of NHE1, by cariporide treatment. For pHi measurments at least 30 cells were analyzed. b Efficiency of knockdown of indicated targets at the mRNA and protein levels, following reverse transfection of MCF7 cells with the indicated siRNAs. qPCR was repeated at least three times with three replicates. c The effect of gene inhibition in normal and low extracellular pH (pHe) shown for naïve and AA MCF7 breast cancer cells. Similar color code to Fig. 3 is applied. At low pHe where the lowest pHi was obtained there is a large reduction in the viability of cells. In AA cells, only the selective and pH-specific targets (GAPDH, GPI, and ACAT2) achieve amplified anti-proliferative effects following NHE1 inhibition, despite the smaller reduction in the pHi of these cells. PFAS, a selective but not pH-specific target, is similar to control cells following NHE1 inhibition. Knockdown of RPIA had a weak effect in naïve cells and no/opposite effects in AA cells. The viability assay was done three times with four replicates each time. The bars depict the mean and the error bars depict the standard deviation of the mean