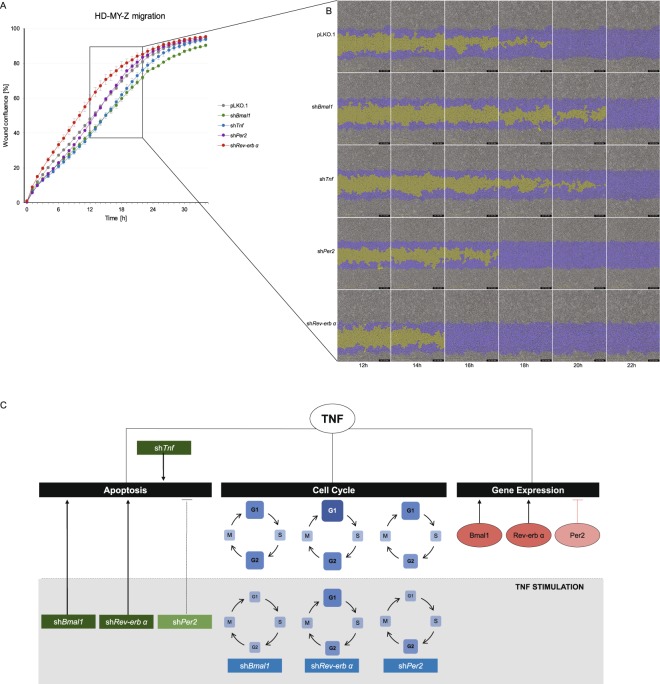
Figure 6.
Tnf and core-clock genes affected cell migration in the HL cell line HD-MY-Z. (A) Migration properties of pLKO.1 empty vector and KD HD-MY-Z cell lines (shBmal1, shTNF, shPer2 and shRev-erbα), measurements were obtained using a scratch wound assay for the IncuCyte S3 Live Cell System Analysis. Quantification was performed by measuring the relative wound confluence over the course of 34 hours. (n = 3, mean ± SEM). (B) Partial representation of the scratch wound assay for all HD-MY-Z KD derived cell lines in the course of 12–22 hours. Images were obtained with the IncuCyte S3 Software. Yellow mask indicates the wound border locations. Blue mask indicates the initial scratch wound area. (C) A model for the bi-directional role of TNF and the core-clock in regulating the molecular and cellular characteristics in HL. TNF regulates gene expression, cell cycle and apoptosis by interacting with the core-clock elements Bmal1, Per2 and Rev-erbα (orange circles). The grey area represents stimulatory effects of TNF on KD cell lines. TNF stimulation differentially affects the cell cycle phases of the KD cell lines, as illustrated by the different sizes and colour of each blue square (compared to pLKO.1). Cellular apoptosis is influenced by TNF stimulation in shRNA cell lines leading to its activation (shBmal, shRev-Erb) or inhibition (shPer2).