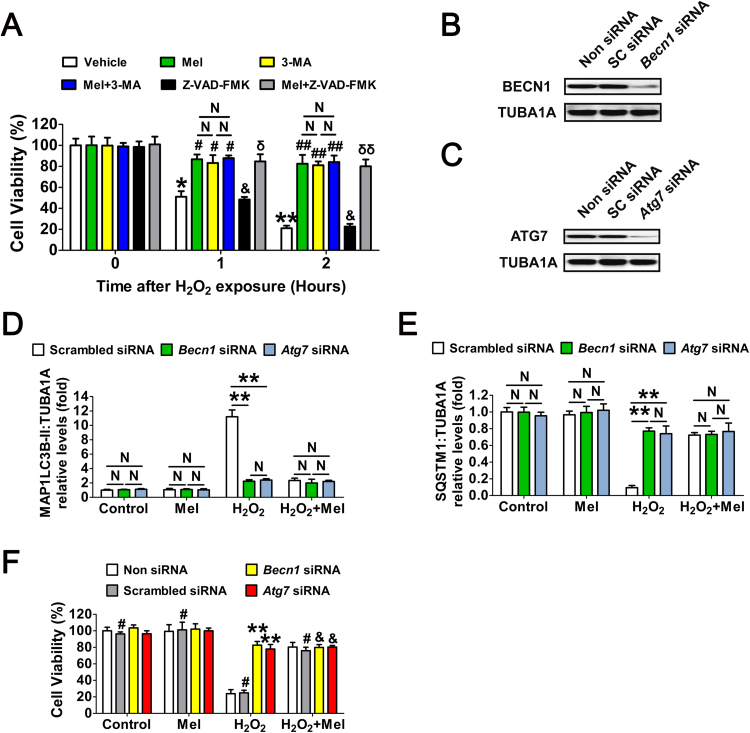
Fig. 3.
Melatonin preferentially inhibits the autophagic death to prevent oxidative stress-induced GC injury. (A) GCs with 24 h of melatonin (10 μM) treatment were rinsed in PBS, and then exposed to H2O2 (200 μM) for 2 h. The autophagy inhibitor 3-MA (10 mM), or the apoptosis inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (50 μM) were added 1 h prior to H2O2 incubation. Cell viability was determined using the CCK-8 assay. Data represent mean ± S.E; n = 3 in each group. *P < 0.05 (**P < 0.01) vs. vehicle group at 0 h. # Represents P < 0.05 (## Represents P < 0.01) vs. H2O2-only-treated cells. & Represents P > 0.05 vs. H2O2-only-treated cells. N, not significant, P > 0.05. δ Represents P < 0.05 (δδ Represents P < 0.01) vs. Z-VAD-FMK-treated cells. (B and C) Primary cultured GCs remained as an untreated control or were transfected with Becn1 siRNA, Atg7 siRNA or scrambled control siRNA for 48 h. The protein levels of BECN1 and ATG7 were evaluated using western blotting. TUBA1A served as the control for loading. (D and E) GCs transfected with Becn1 siRNA, Atg7 siRNA or scrambled control siRNA for 24 h were cultured in media containing 10 μM melatonin for another 24 h before 2 h of H2O2 (200 μM) incubation. Cell lysates were then collected for western blotting assay. The MAP1LC3B-II accumulation and SQSTM1 degradation were quantified by densitometric analysis. TUBA1A served as the control for loading. Data represent mean ± S.E; n = 3 in each group. **P < 0.01; N, not significant, P > 0.05. (F) Cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay in GCs with the indicated treatments as described above. ** Represents P < 0.01 compared to ‘Non siRNA’ condition. # Represents P > 0.05 compared to ‘Non siRNA’ condition. & Represents P > 0.05 compared to ‘H2O2 +melatonin’ condition.