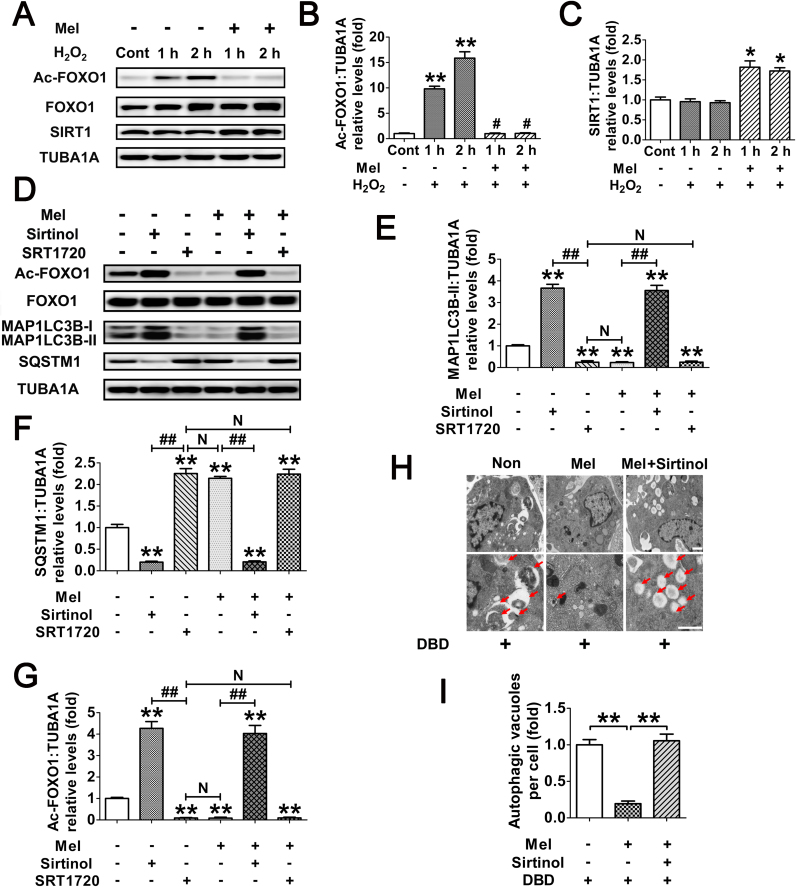
Fig. 9.
Deacetylation of FOXO1 via the melatonin-SIRT1 signaling inhibits FOXO1-dependent autophagy in GCs. (A) GCs were cultured with 10 μM melatonin for 24 h, washed in PBS, and then exposed to H2O2 incubation for 1 or 2 h. The protein level of acetylated FOXO1 (Ac-FOXO1), total FOXO1 and the deacetylase SIRT1 was determined by western blotting. (B and C) The relative expression of Ac-FOXO1 and SIRT1 were quantified using densitometric analysis. Data represent mean ± S.E; n = 3. ** Represents P < 0.01 compared to control group. # Represents P > 0.05 compared to control group. (D) GCs transfected with FOXO1N208A,H212R plasmid for 24 h were grown in medium containing 10 μM melatonin. 24 h later, cells were cultured for another 2 h in the presence or absence of Sirtinol (100 μM) or SRT1720 (100 μM). The expression of Ac-FOXO1, total FOXO1, MAP1LC3B and SQSTM1 was then detected by western blotting. (E–G) Quantification of FOXO1 acetylation, MAP1LC3B-II accumulation and SQSTM1 degradation. TUBA1A served as a loading control. Data represent mean ± S.E; n = 3. (H) GCs transfected with FOXO1N208A,H212R plasmid for 24 h were cultured for another 24 h in the presence or absence of 10 μM melatonin before 2 h of Sirtinol (100 μM) treatment. Cells were then collected for TEM imaging of the autophagic structures. Bar, 0.8 µm. Enlarged images (below) show clearer autophagic vacuoles (red arrows). (I) Number of autophagic vacuoles per cell section in GCs. Bar graphs are mean ± S.E of results from 10 cell sections. **P < 0.01 (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.).