Figure 5. AIH‐Hc induced sensory LTF involves heat‐sensitive TRPV1 receptors and increases CB heat sensitivity.
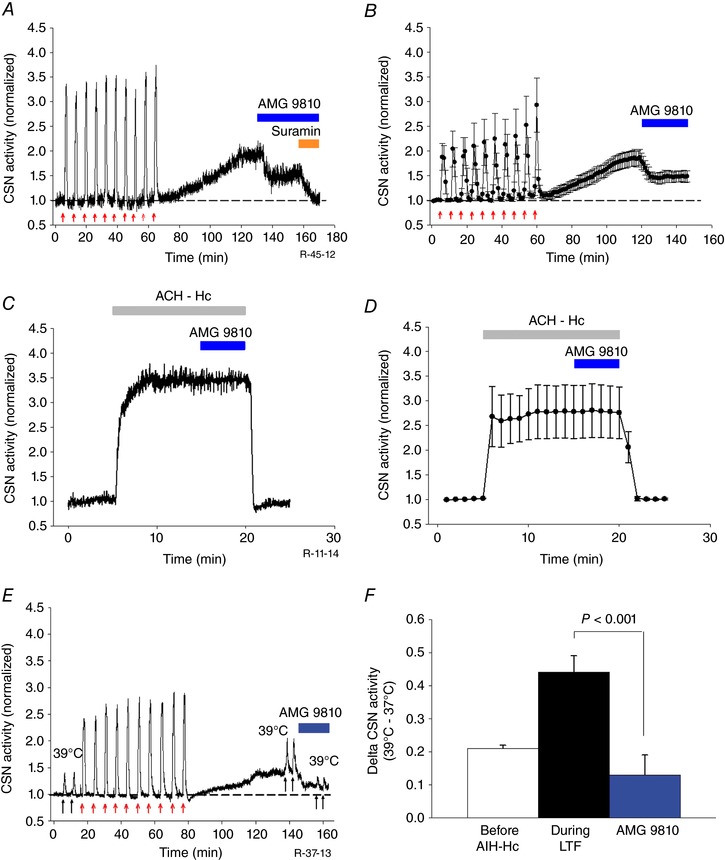
A, integrated CSN activity from one preparation showing ∼50% of sensory LTF induced by AIH‐Hc is inhibited by TRPV1 receptor antagonist AMG 9810 (10 μm; blue bar). The facilitated activity that remained was completely suppressed by suramin (100 μm; orange bar). B, average integrated CSN activity showing the effect of AMG9810 on sensory LTF (mean ± SEM; n = 5). C and D, integrated CSN activity from one preparation and average data (mean ± SEM; n = 6; P = 0.97) showing that AMG 9810 had no effect on the response to 10 min of acute continuous hypoxia‐hypercapnia (ACH‐Hc) (grey bar). E, integrated CSN activity from one preparation showing responses to temperature challenges (37 to 39°C for 1 min each; black arrows) before, 60 min after 10 episodes of AIH‐Hc (red arrows) and, subsequently, with partial inhibition of sensory LTF with TRPV1 antagonist AMG9810 (10 μm). F, summary of CSN responses following temperature challenge. Data are the mean ± SEM; n = 5.
