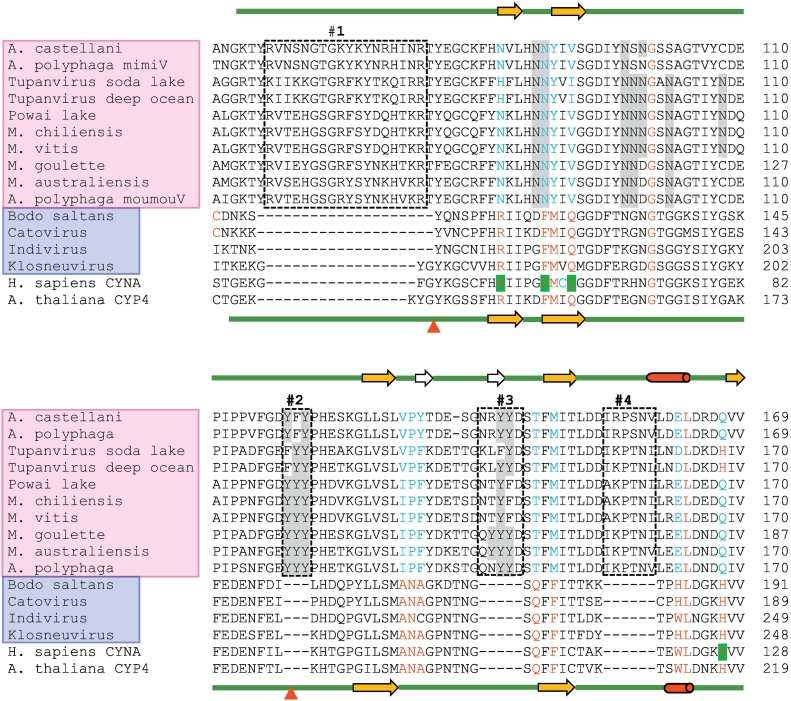
Fig. 3.
Distinctive sequence features of the Klosneuvirus and Mimivirus cyclophilins. Retrieval of the sequences and multiple alignment have been described in detail under Methods. Only the relevant portion, important for PPIase catalytic activity, is shown. For space constraints, the virus names are written in arbitrary shorthand, since no abbreviated nomenclature system has yet been established for the giant viruses. The full GenBank names of the viruses, the corresponding accession numbers (also in Fig. 1), and total number of amino acids (aa) in the full-length protein are as follows (from top to bottom): Acanthamoeba castellanii mamavirus (AEQ60805.1; 234 aa); Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus, Kasai strain (AAV50868.1; 234 aa; the sequence BAV62707.1 of the shirakomae strain was identical, and therefore, excluded); Tupanvirus soda lake (AUL77649.1; 245 aa); Tupanvirus deep ocean (AUL78930.1; 249 aa); Powai lake megavirus (ANB50819.1; 245 aa); Megavirus chiliensis (YP_004894774.1; 246 aa); Megavirus vitis (AVL94038.1; 244 aa); Moumouvirus goulette (AGF85091.1; 262 aa); Moumouvirus australiensis (AVL95022.1; 242 aa); Acanthamoeba polyphaga moumouvirus (YP_007354597.1; 242 aa); Bodo saltans virus (ATZ80220.1; 228 aa); Catovirus CTV1 (ARF08362.1; 226 aa); Indivirus (ARF09529.1; 286 aa); Klosneuvirus (likely 284 aa; see Fig. 2). Cellular Homo sapiens cyclophilin A (P62937.2; 165 aa) and Arabidopsis thaliana CYP4 (NP_001154684; 313 aa) are also included for comparison. The Mimivirus and Klosneuvirus orthologs are boxed in pink and purple, respectively, and the inserts in Mimivirus sequences are also boxed by dotted lines and numbered #1 to #4. The secondary structural elements of the two groups are drawn respectively on top and bottom: orange arrow (β-strand), red cylinder (α-helix); green line (linker sequences outside helices and strands). Two Mimivirus-specific short helices are shown as white arrows. The 13 consensus residues, important for PPIase activity [26], are in red colour; those that are different from consensus are in teal colour. Mutation of the green highlighted residues in human CYNA (R55, F60, Q63, H126) into Ala destroyed PPIase activity but not chaperone activity [9]. The two red triangles are common sites of peptide insertion in a variety of cyclophilins (detailed under Discussion). Asn (N) and Tyr (Y), relatively abundant in several loop regions, are highlighted in grey.