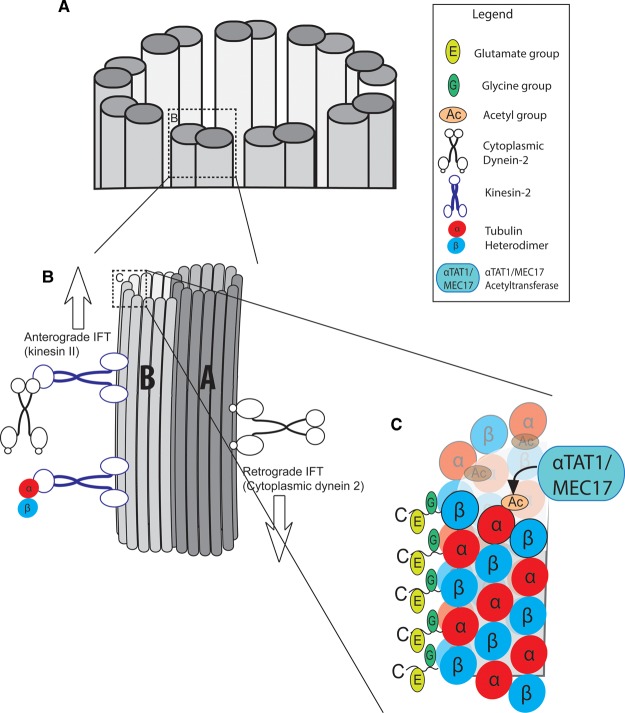
Figure 2. Composition and arrangement of axoneme microtubules.
(A) Cross-section of a generic non-motile axoneme is depicted, composed of nine microtubule doublets. (B) A doublet consists of a complete A-tubule and a partial B-tubule. The B-tubule binds the anterograde IFT motor protein kinesin-II, which transports cargos including tubulin subunits and the retrograde motor cytoplasmic dynein 2. The A-tubule binds the retrograde IFT motor dynein [12]. (C) AxoMTs are targets of microtubule PTMs, which affect MT stability and dynamics. K40 acetylation (orange) occurs on α-tubulin on the lumenal face of the tubule, catalyzed by αTAT1. Glycylation (green) and glutamylation (yellow) occur on the C-terminal tails of α- and β- tubulin.