Figure 2.
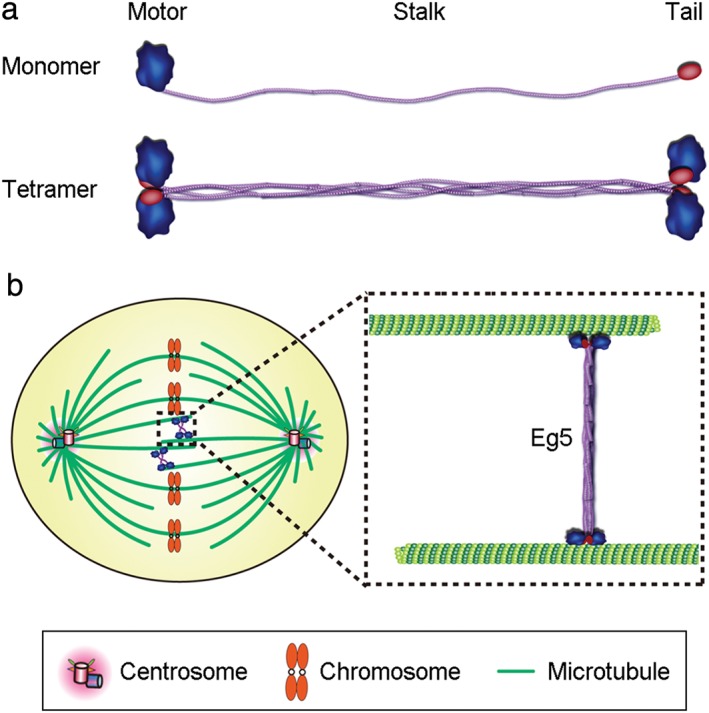
Eg5 structure and function. (a) An Eg5 monomer contains a motor domain, a stalk domain, and a tail domain (top). Four Eg5 monomers form a homotetramer via interactions between the stalk domains (bottom). (b) Schematic model showing that the Eg5 tetramer crosslinks and slides apart anti‐parallel microtubules, contributing to bipolar spindle formation and maintenance.
