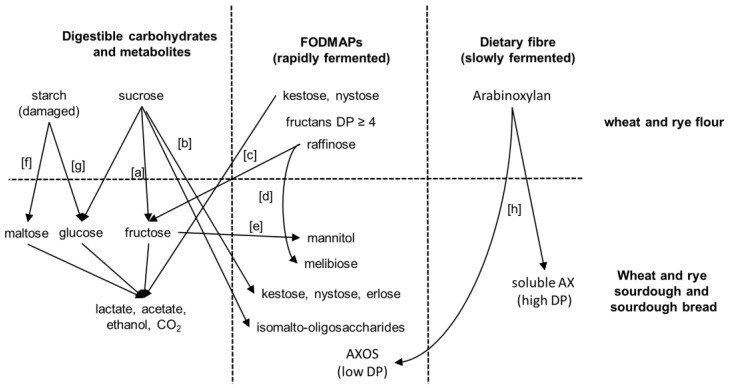
Figure 1.
Conversion and generation of fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) in wheat and rye sourdoughs. Sucrose hydrolysis by yeast invertase or fructosidases of lactic acid bacteria [a]. Oligosaccharide formation by glucansucrases to form isomalto-oligosaccharides, or by fructansucrases to form kestose, nystose, and erlose from sucrose [b]. Kestose and nystose degradation by yeast invertase or by intracellular (phospho)-fructosidases of lactic acid bacteria [c]. Raffinose conversion by yeast invertase and levansucrase from lactic acid bacteria [d]. Fructose conversion by mannitol-dehydrogenase from heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria [e]. Starch conversion to maltose and glucose by flour amylases and gluco-amylase [f,g]. Exogenous xylanases are used in baking to increase the amount of soluble pentosane (arabinoxylan, AX) to improve bread properties, which can produce low DP arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (AXOS) along soluble high-DP arabinoxylan fragments [h].