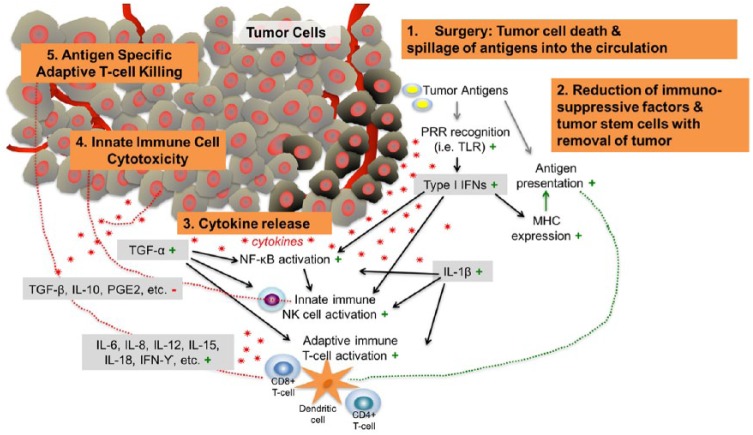
Figure 4.
Proposed depiction of abscopal events that contribute to antitumor efficacy post surgery in combination with immunotherapy. In addition to tumor cell death, surgical tumor removal or debulking likely induces secretion of cytokines and chemokines that can kill cancer cells directly and also recruit and activate innate and adaptive immune cells that attack the tumor. Most of the downstream effects of surgery are favorable for tumor therapy (indicated by the green plus signs), which counteract immunosuppressive molecules (red minus sign) in the tumor microenvironment.