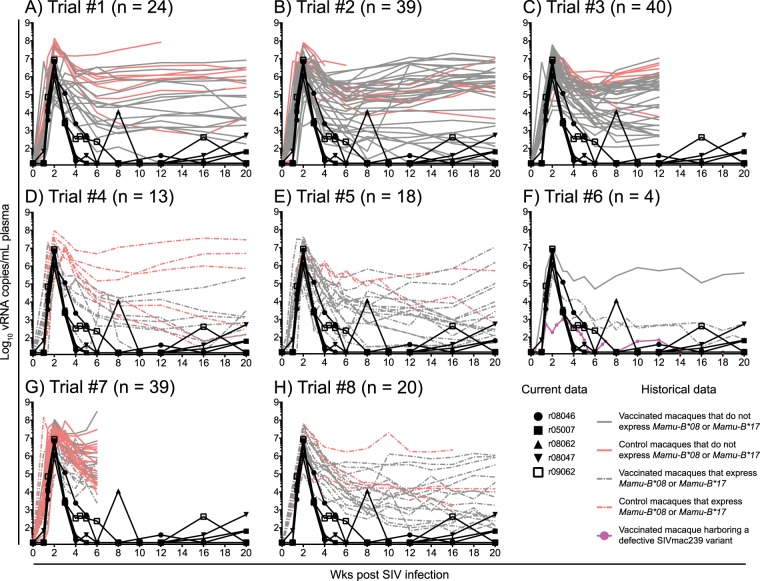
FIG 8.
Viral loads in the five group 2 controllers compared to those in RMs historically infected with SIVmac239. The outcome of SIVmac239 infection in the five group 2 vaccinees that manifested early control of viral replication was compared to those of 197 RMs that were rectally infected with SIVmac239 as part of eight SIV vaccine trials conducted by our group. The historical VLs for each independent SIV vaccine trial are plotted in panels A to H and include both vaccinated (gray lines) and control (salmon lines) RMs. VLs from RMs that expressed MHC-I alleles associated with elite control of SIV infection (i.e., Mamu-B*08 and Mamu-B*17) are shown in dashed lines. VLs from RMs that did not express these protective MHC-I alleles are shown in solid lines. To better visualize the early control of viral replication manifested by the five group 2 vaccinees, their VLs (black lines) were also plotted in each panel. Additionally, only the first 20 weeks of SIV infection are shown in each graph. (A) In trial 1, 24 RMs were vaccinated with env, gag, vif, rev, tat, and nef delivered by either rRRV alone or rRRV followed by two boosts with rAd5 and rVSV. Eight RMs served as the controls for the challenge phase (M. A. Martins, D. C. Tully, N. Pedreño-Lopez, B. von Bredow, M. G. Pauthner, Y. C. Shin, M. Yuan, N. S. Lima, D. J. Bean, L. Gonzalez-Nieto, A. Domingues, M. J. Gutman, H. S. Maxwell, D. M. Magnani, M. J. Ricciardi, V. K. Bailey, J. D. Altman, D. R. Burton, K. Ejima, D. B. Allison, D. T. Evans, E. G. Rakasz, C. L. Parks, M. C. Bonaldo, S. Capuano III, J. D. Lifson, R. C. Desrosiers, T. M. Allen, D. I. Watkins, unpublished data). (B) The details of this experiment were published recently (27). Briefly, 32 RMs were vaccinated with an EP rDNA/rAd5/rVSV/rRRV regimen encoding four different sets of SIV inserts. Eight RMs served as the controls for this experiment. One vaccinee did not get infected, so VL traces for 39 RMs are shown in the graph. (C) The details of this experiment were published recently (71). Briefly, four different mixed-modality vaccine regimens were used to deliver minigenes of SIV gag, vif, and nef to 32 RMs. Eight RMs served as the controls for this experiment. (D) Ten Mamu-B*08+ RMs were vaccinated with a rAd5/rVSV/rRRV regimen including vif, rev, tat, and nef, and six MHC-I-matched RMs served as the controls for the challenge phase (Martins et al., unpublished). Three vaccinees did not acquire SIV infection in this experiment, so VL traces for 13 RMs are shown in the graph. (E) The details of this experiment were published recently (72). Briefly, 16 Mamu-B*08+ RMs were vaccinated with an EP rDNA/rYF17D/rAd5 regimen containing nef, and two MHC-I-matched macaques served as the controls for the challenge phase. (F) The details of this experiment were published recently (30). Four RMs, two of which were Mamu-B*08+, were vaccinated with an EP rDNA/rYF17D/rRRV regimen containing either gag or nef. For unknown reasons, the animal highlighted in pink harbored a nef deletion SIV variant as early as week 2 p.i. The replicative fitness cost imposed by this nef deletion likely underlies the stringent control of viral replication manifested by this animal. (G) Twenty RMs were vaccinated with an EP rDNA/recombinant vaccinia/rVSV/rAd5/rRRV regimen encoding vif only. Twenty MHC-I-matched RMs served as the controls for the challenge phase. Eight vaccinees and nine control RMs expressed either Mamu-B*08 or Mamu-B*17 (Martins et al., unpublished). One vaccinee did not acquire SIV infection, so VL traces for 39 RMs are shown in the graph. (H) The details of this experiment were published elsewhere (21). Briefly, 16 Mamu-B*08+ RMs were vaccinated with an rYF17D/rAd5 regimen including either vif and nef minigenes containing Mamu-B*08-restricted epitopes or regions of the SIV proteome lacking epitopes restricted by Mamu-B*08. Four MHC-I-matched RMs served as the controls for the challenge phase.